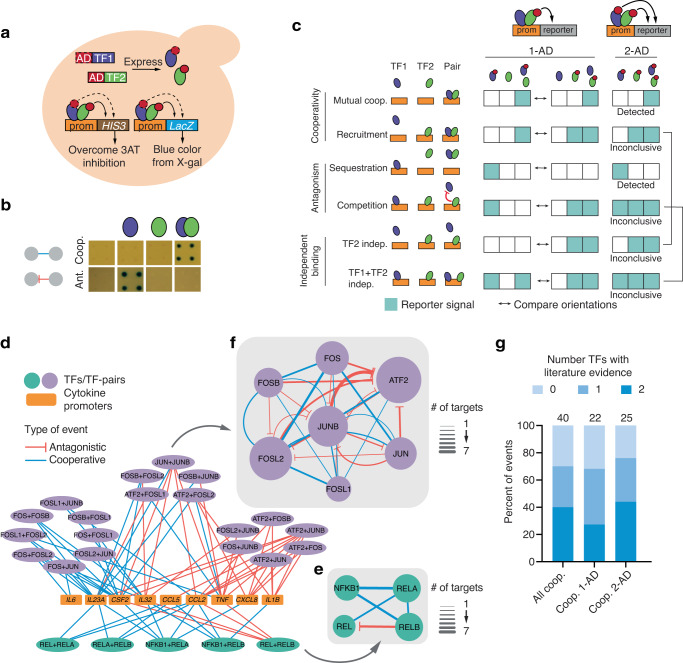
Fig. 1. Paired yeast one-hybrid (pY1H) assays.
a Schematic of pY1H assays. A DNA-bait yeast strain with a DNA sequence of interest (e.g., a promoter) cloned upstream of the HIS3 and lacZ reporter genes is mated with a TF-pair prey strain expressing two TFs fused or not to the Gal4 activation domain (AD). If an AD-containing TF binds the DNA region of interest, reporter expression will allow the yeast to grow in media lacking histidine and in the presence of the His3p inhibitor 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole (3AT), and turn blue in the presence of X-gal. b pY1H assays detect cooperative and antagonistic interactions by comparing single-TF and TF-pair yeast strains. c Comparison between 1-AD and 2-AD screen designs for different cooperative (mutual cooperativity and recruitment), antagonistic (sequestration and competition), and independent DNA binding modalities. Teal boxes indicate cases where reporter activity is expected. While the 1-AD design can distinguish between the six indicated binding modalities if reciprocal AD orientations are tested, the 2-AD design can only detect mutual cooperativity and sequestration. d–f Results of pY1H screen between NF-κB and AP-1 TF-pairs and cytokine gene promoters. d Main network shows connections between TF-pairs and cytokine promoters. e, f Cooperative and antagonistic relationships between NF-κB (e) and AP-1 (f) TFs. Node size indicates the number of binding events for that TF. Edge width represents the number of cooperative or antagonistic events involving a specific TF-pair. g Overlap of NF-κB and AP-1 pY1H interactions with the literature. Numbers above each bar reflect the number of binding events assessed in each category. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.