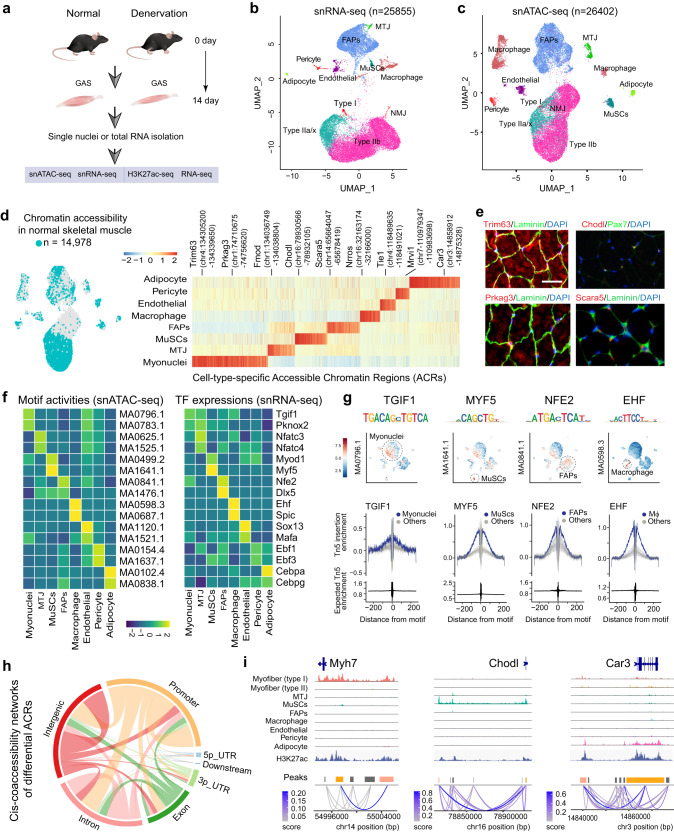
Fig. 1. An atlas of cis-regulatory networks in normal skeletal muscle.
a Experimental scheme. b Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) plot presents 11 nuclear clusters derived from snRNA-seq data of GAS muscle nuclei in three normal and three denervated mice (n = 25,855 nuclei). Clusters are distinguished by color and labeled based on their nuclear identities. c UMAP visualization of snATAC-seq data from GAS muscle nuclei of three normal and three denervated mice (n = 26,402 nuclei), annotated based on chromatin accessibility to highlight accessible chromatin regions (ACRs). d Left: UMAP plot displaying ACRs in normal muscles. Right: Heatmap illustrates the average count of Tn5 insertion sites within DARs for each nuclear type in normal GAS muscle. Signature genes are highlighted at the top, with additional signature gene loci provided in Supplementary Data 1. e Representative immunostaining images of proteins encoded by selected genes (Trim 63, Chodl, Prkag3, and Scara5) in the GAS muscle of a normal mouse. Scale bar: 25 μm. f Z-score heatmaps display motif activity (left) and the associated TF gene expression (right) for each nuclear type. For the complete list of all 579 motifs and their best-matched TFs, please see Supplementary Data 2. g UMAP plots display the activity of cell-type-specific motifs for four selected transcription factors (TFs) in the upper panel, accompanied by their respective footprint plots in the lower panel. The footprint lines are color-coded based on cell identity. h Cis-coaccessibility networks (CCANs) visualizing interactions among cell-type-specific ACRs. Source data are provided as a Source data file. i Aggregated cell-type chromatin accessibility, H3K27ac signal, and CCANs around selected gene loci. Orange indicates the promoter region, while pink highlights distal intergenic regions. Links represent co-accessibility between ACRs, with color density indicating the strength of interaction.