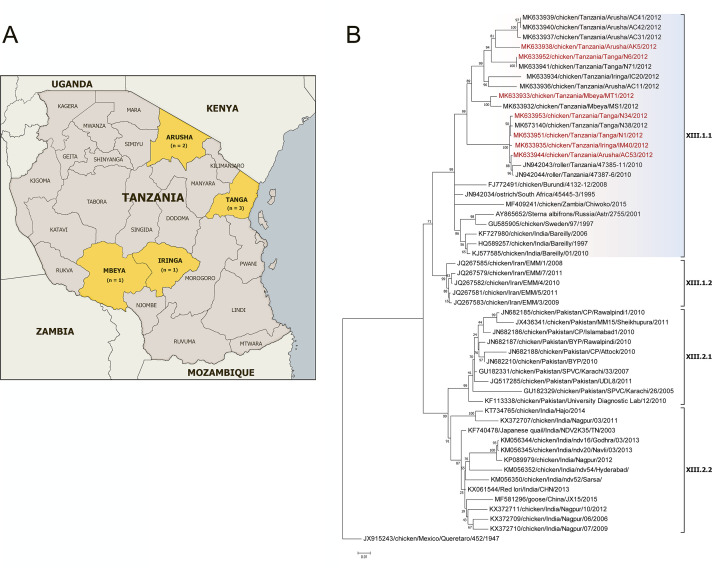
Fig 1.
(A) Locations for the live bird market surveillance. (B) Phylogenetic analysis of NDV isolates of genotype XIII based on the complete fusion gene sequences constructed with the Maximum Likelihood method based on the General Time Reversible model in MEGA version 7.0.26. The tree with the highest log likelihood (−9896.03) is shown. The percentage of trees in which the associated taxa clustered together is shown next to the branches. Initial tree(s) for the heuristic search were obtained automatically by applying Neighbor-Join and BioNJ algorithms to a matrix of pairwise distances estimated using the Maximum Composite Likelihood (MCL) approach and then selecting the topology with superior log likelihood value. A discrete Gamma distribution was used to model evolutionary rate differences among sites [five categories (+G, parameter = 0. 4735)]. The rate variation model allowed for some sites to be evolutionarily invariable [(+I), 38.62% sites]. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured in the number of substitutions per site. The analysis involved 54 nucleotide sequences (sequence from genotype XVI is included as an outgroup). All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. There were a total of 1,662 positions in the final dataset. The isolates used in this study are shown in red.