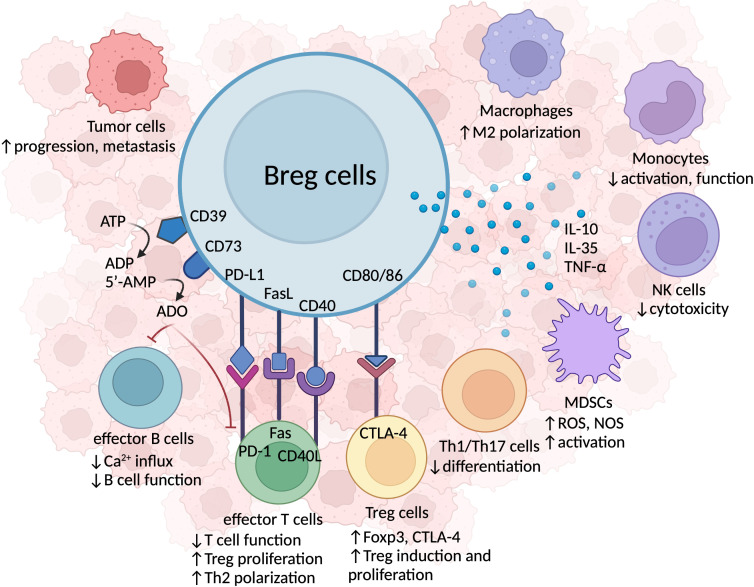
Figure 2.
The immunosuppressive mechanisms of Breg cells in HNSCC. Breg cells secrete immunosuppressive cytokines, including IL-10, IL-35, and TNF-α, which inhibit anti-tumor immune activity, foster immunosuppressive TILs, and facilitate tumor progression and metastasis. The co-expression of CD39 and CD73 surface proteins permits Breg cells to hydrolyze ATP to adenosine (ADO), which acts on effector T and B cells, reduces Ca2+ influx, and results in the malfunction of effector immune cell. Breg cells also form cell-cell contacts with other TILs. Breg cells can induce anti-tumor T cell malfunction via PD-L1-PD-1 axis, or Fas/FasL binding. Breg cells and effector T cells interact via CD40/CD40L to promote Th1/Th2 cell polarization and Treg cell proliferation. Breg cells are also capable of forming cellular contacts with other immunosuppressive TILs, such as MDSCs and Treg cells. The CD80/CD86 marker expressed on Breg cells binds to CTLA-4 on Treg cells, inducing Treg cell proliferation.