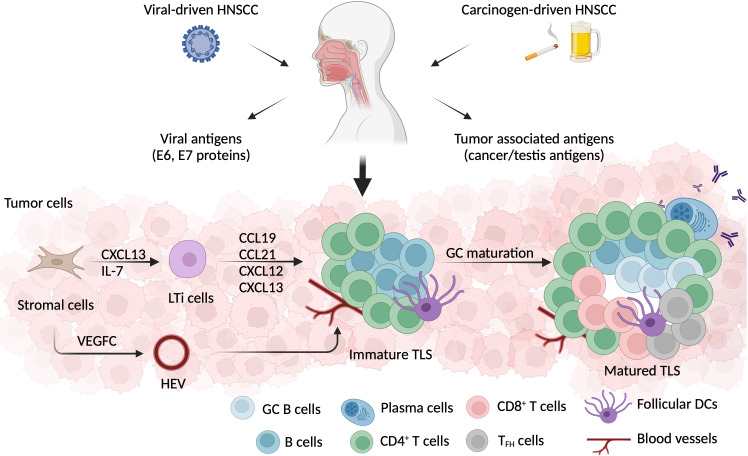
Figure 3.
TLS formation in HNSCC. HNSCC can be induced by either viral infection, or environmental carcinogens, such as smoking or excessive alcohol consumption. Besides tumor associated antigens, the HPV+ HNSCC microenvironment also exposes E6 and E7 viral antigens. TLS, a crucial ectopic lymphoid cell formation, develops in the early stage of tumorigenesis. Local stromal cells that have been activated secret CXCL13 and attract lymphoid tissue inducer (LTi) cells. LTi cells produce a series of chemokines, including CCL19, CCL21, CXCL12, and CXCL13, which aid in the recruitment of LTi cells and lymphocytes. Additionally, stromal cells secrete VEGF-C, which promotes HEV development in the vicinity of TLSs. After germinal center (GC) maturation, a well-defined TLSs is formed with a CD3+ T cell zone composed of CD4+, CD8+, and TFH cells, and a CD20+ B cell zone comprising GC B cells, memory B cells, and plasma cells. Besides lymphocytes, follicular DCs, fibroblasts, and neovascular cells are also involved in the process of TLS formation.