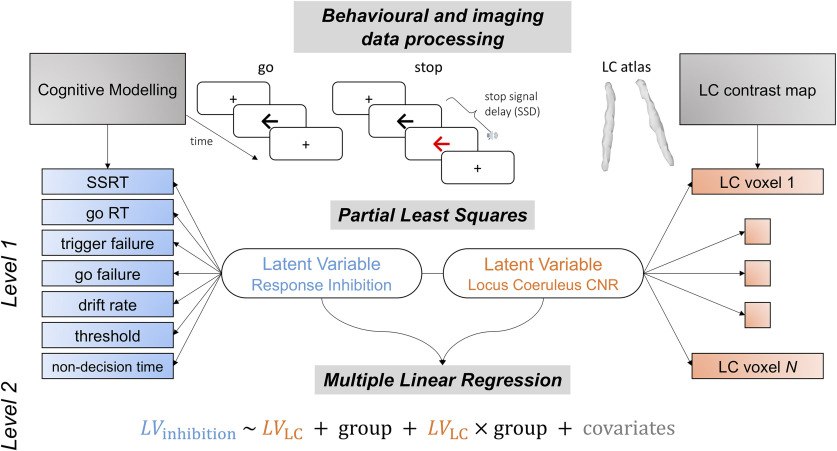
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of data analysis pipeline. The trial-by-trial stop signal task performance was subjected to a two parametric race model following ex-Gaussian and shifted Wald distributions. An array of behavioral parameters were estimated hierarchically from the models for both stop and go response, including SSRT, go RT, trigger failure, go failure, drift rate (ν), response threshold (B), and nondecision time (t0). These parameters altogether provided more mechanistic understanding of response inhibition. The LC integrity was assessed by computing voxel-wise CNR and extracted using an independent LC probability atlas. The multivariate relationship between LC integrity and response inhibition was then examined using PLS on resulting behavioral and imaging matrices from previous data processing steps. Significant pairs of latent variables were identified with the permutation test. The contribution of LC in response inhibition was finally confirmed in linear regression models with individual subject loading scores on the inhibition latent variable as dependent variable, loading scores on the LC latent variable, group and nuisance covariates as predictors.