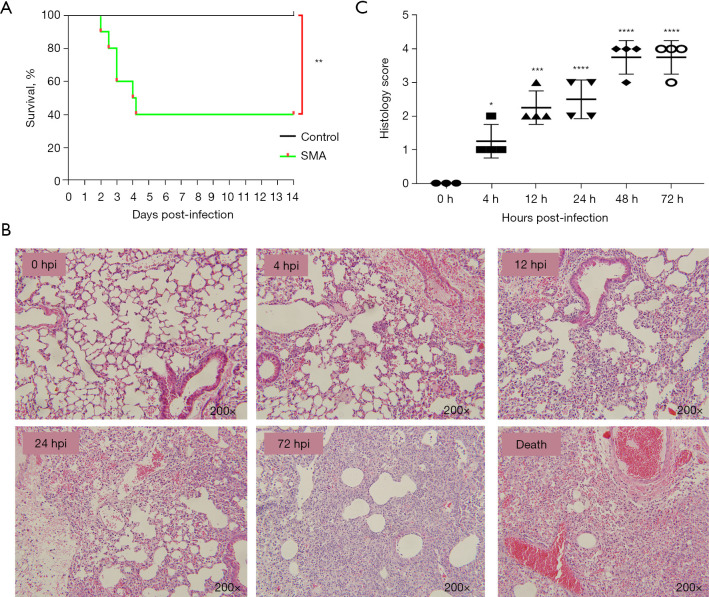
Figure 1.
Survival curves and histopathological analysis of lung tissue of mice infected with SMA via aerosol intratracheal inoculation. (A) Survival curves of mice after pulmonary infection. Mice were challenged with either PBS or 5×108 CFU/mL of the SMA strain (K279a) (n=10 per group). Survival differences between infected and control mice were statistically significant (**, P<0.01; log-rank test). In a repeat experiment, similar results were obtained. (B) Histopathological analysis and H&E staining of the lungs (200×). Histopathological changes assessed using H&E staining revealed neutrophil infiltration in lung tissue at 4 hpi, followed by a significant increase in the infiltration of neutrophils and monocytes at 12–72 hpi. At 72 hpi, there was massive destruction of alveolar structures, thickening of alveolar septa, and hemorrhage. (C) Pathological scores of lung sections in mice were determined at 0, 4, 12, 24, 48, and 72 hpi. *, P<0.05; ***, P<0.001; ****, P<0.0001 compared with 0 hpi. SMA, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; hpi, hours post-infection; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; CFU, colony forming units; H&E, hematoxylin & eosin.