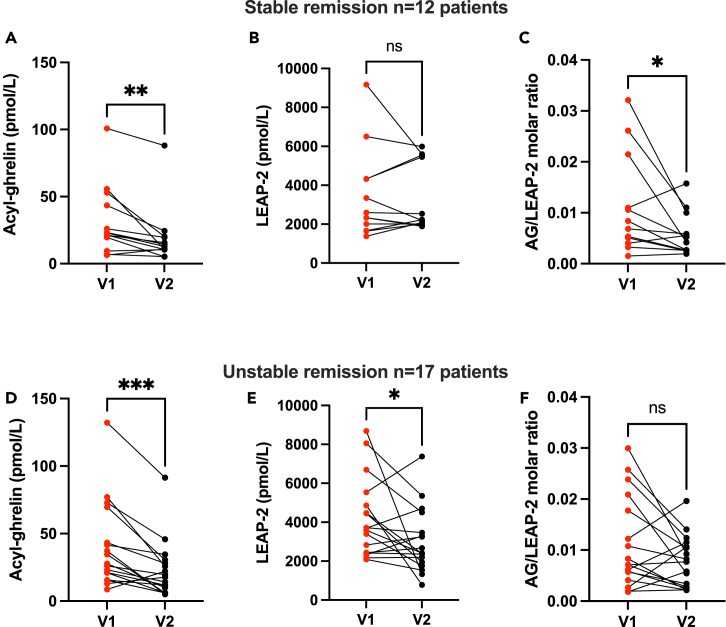
Figure 4.
Higher LEAP-2 levels at admission than after discharge is associated with unstable remission
AG/LEAP-2 evolution with refeeding in patients with stable (n = 12, BMI>18.5 kg/m2, A–C) and unstable remission (n = 17, BMI<18.5 kg/m2, D–F) 6 months after discharge. AG levels decreased after refeeding in stable (A) and unstable (D) patients. LEAP-2 levels remained stable during refeeding in patients with stable remission at 6 months (B) but significantly decreased in patients with unstable remission (E). The AG/LEAP-2 molar ratio decreased with refeeding in patients with stable remission (C) but did not significantly differ between before and after refeeding in patients with unstable remission (F). Data are expressed as individual values and were analyzed using paired Student’s t test or Mann-Whitney: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. AG: Acyl-ghrelin. LEAP-2: Liver-Expressing Antimicrobial Peptide-2.