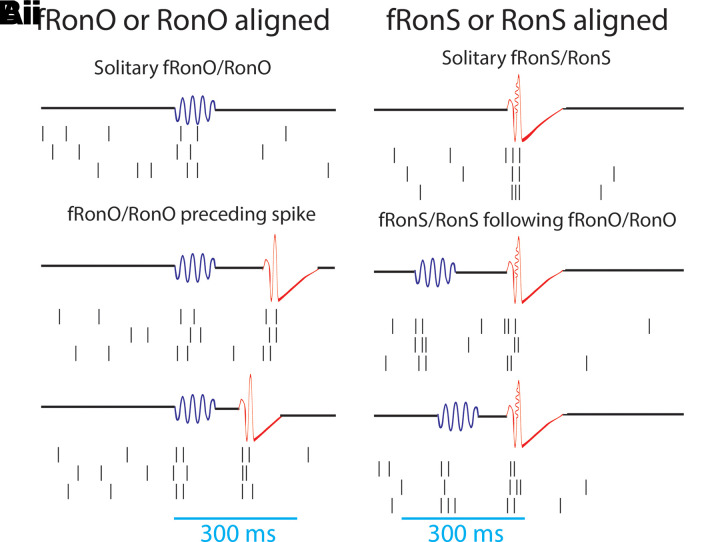
Figure 1.
Schematic of the analytical methods comparing unit APs with fRonO (A, blue), RonO (A, blue), fRonS (B, red) and RonS (B, red), as well as the temporal coincidence of these HFO event types within 300 ms (Aii, Bii). AP trains were either temporally aligned to the onset for fRonO/RonO events (A) or the onset of fRonS/RonS events (B). Events were considered solitary if a fRonO or RonO did not precede a fRonS/RonS by <300 ms, and sharp spikes, lacking an HFO, were also accounted for (Aii). HFO event-unit trials aligned to fRonO/RonO events served to assess changes in excitability between solitary fRonO/RonO (Ai) and the fRonO/RonO that preceded (<300 ms) spikes (Aii). In contrast, HFO event-unit trials aligned to fRonS/RonS (B) assessed the changes in excitability between solitary fRonS/RonS (Bi) and fRonS/RonS that followed (<300 ms) fRonO/RonO (Bii).