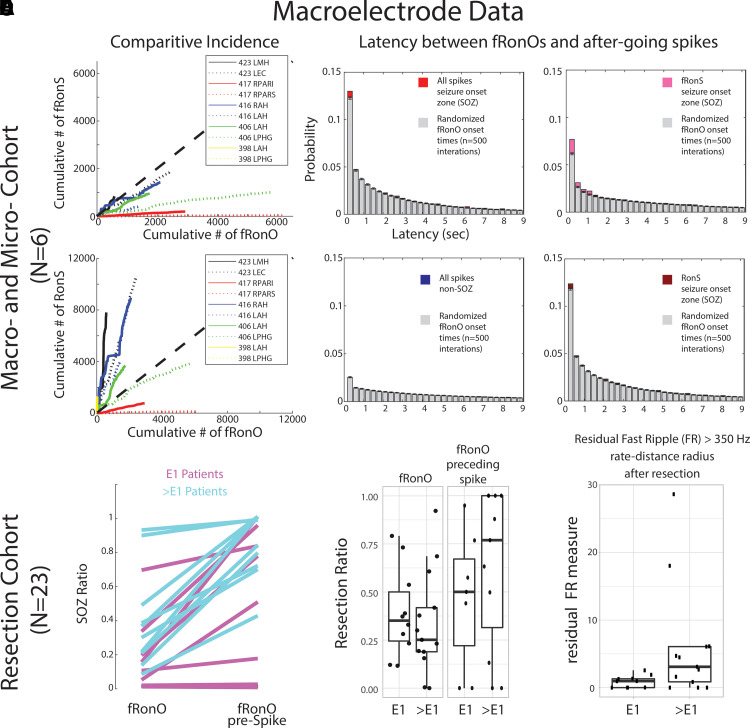
Figure 5.
fRonO preceding (<300 ms) epileptiform spikes occur mostly in the SOZ; however, resection of cortical territory generating fRonO with after-going spikes does not correlate with seizure freedom. In the paired macroelectrode and microelectrode cohorts, (A) comparative incidence of fRonO with (fRonS, top), as well as fRonO with (RonS, bottom) in 10 macroelectrode channels in the SOZ calculated in bins of 60 s over the recording duration. Note that for most channels, multiple fRonOs occur before a fRonS is detected. However, RonS are generated in greater number than fRonO. (B) Normalized histogram of the latency between spike onset and fRonO in individual iEEG channels when computed using all spikes in the SOZ (red bars, n = 41 861 fRonO), all spikes in the non-SOZ (blue bars, n = 52 136 fRonO), only fRonS in the SOZ (pink bars) and only RonS in the SOZ (dark red bars). Latencies computed with boot-strapping statistics (see ‘Materials and methods’ section, n = 500 surrogates, grey bars) indicated that fRonO in the <300 ms bin exceeded chance (z-score = 4.61, P < 1e−5) but were less than chance in the non-SOZ (z = −7.72, P > 0.05, blue). The most significant effect was seen for fRonO with after going fRonS (z = 11.61, ). (C–E) Data taken from a cohort of 23 patients with stereo-EEG recordings, but no microelectrodes placed, who underwent resections. (C) The within-patient differences in the proportion of events in the SOZ for fRonO events compared with fRonO events preceding (<300 ms) spikes for patients with a seizure-free Engel 1 (E1) outcome (magenta) and non-seizure-free patients (cyan, >E1, Engel 2–4). The proportion of fRonO events preceding spikes in the SOZ was significantly higher (rank sum, P < 1e−5). (D) Box plots of the ratio of fRonO (left) and fRonO preceding spike (right) events within the resection margins stratified by post-operative seizure outcome. (E) A spatial graph theoretical measure, the FR rate-distance radius resection difference, that quantifies both the volume and activity of the residual FR generating tissue remaining after resection that was significantly decreased in seizure-free patients (rank sum, P < 0.05). L, left hemisphere; R, right hemisphere; AH/MH, anterior, middle hippocampus; EC, entorhinal cortex; PAR, parietal (sup./inf.); PHG, parahippocampal gyrus.