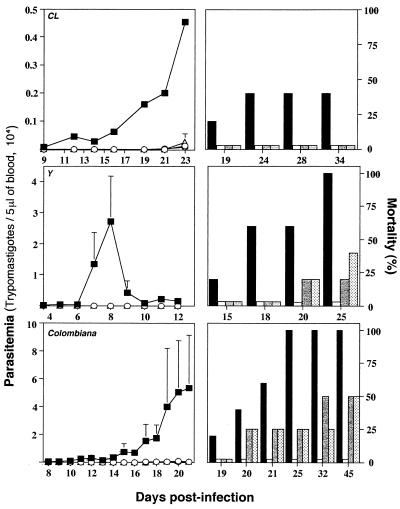
FIG. 3.
Effect of in vivo neutralization of IL-12 or IFN-γ on trypanosomicidal activity of treatment with an optimal dose of Bz during acute phase of infection with different strains of T. cruzi. Swiss-Webster mice were infected with 5,000 trypomastigotes of T. cruzi CL, Y, or Colombiana and were treated with Bz at 100 mg/kg/day for 7 days. Different groups of animals receiving Bz alone (○, white bars) were simultaneously injected with either an anti-IFN-γ MAb (○, gray bars) or an anti-IL-12 MAb (▵, dotted bars) 1 day prior to infection and once a week afterward. The levels of parasitemia (left panels) and the rates of mortality (right panels) were monitored daily until the end of the experiment. Infected and nontreated animals were used as controls (■, black bars). For each datum point presented in the parasitemia curve the average and positive standard deviation are shown for four to five animals per group. Similar numbers of animals were used for the mortality study. This experiment was repeated once and yielded identical results. Some of the parasitemia curves ( , ▵) are not seen in this figure, because none of the treated groups showed an apparent parasitemia. Note that the scale indicating the level of parasitemia (left panels) is different for each T. cruzi strain.