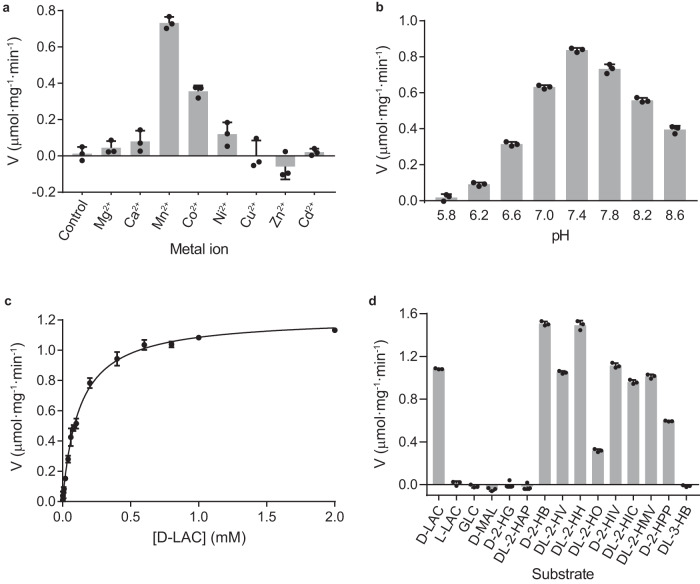
Fig. 1. Enzymatic properties of mLDHD.
a The specific activity of mLDHD to convert D-lactate (D-LAC) to pyruvate (PYR) in the absence and presence of different divalent metal ions (1 mM). b The specific activity of mLDHD towards D-LAC under different pH. c The saturation curve of mLDHD towards D-LAC. d The specific activity of mLDHD towards different substrates and analogs (1 mM). For the racemic substrates, the substrate concentration used in the experiment was doubled and the specific activity was calculated based on the corrected concentration of D-isomer (1/2 of the concentration of racemic substrate). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 3 independent measurements). Source data are provided as a Source Data file. D-LAC D-lactate, L-LAC L-lactate, GLC glycolate, D-MAL D-malate, D-2-HG D-2-hydroxyglutarate, DL-2-HAP DL-2-hydroxy-3-aminopropionate, D-2-HB D-2-hydroxybutyrate, DL-2-HV DL-2-hydroxyvalerate, DL-2-HH DL-2-hydroxyhexanoate, DL-2-HO DL-2-hydroxyocatanoate, D-2-HIV D-2-hydroxyisovalerate, DL-2-HIC DL-2-hydroxycaproate, DL-2-HMV DL-2-hydroxy-3-methylvalerate, D-2-HPP D-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropionate, and DL-3-HB DL-3-hydroxybutyrate.