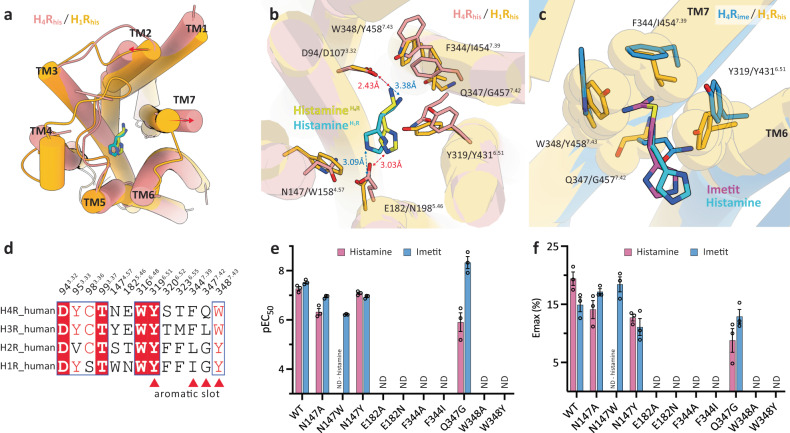
Fig. 4. Subtype selectivity in H4R and H1R.
a, b Structural superposition of H4Rhis (pink) and H1Rhis (orange, PDB 7DFL). (a) top view, (b) the agonist-binding pocket. The helices are shown as cylinders. The histamines of H4R and H1R are indicated by yellow and cyan sticks. c The aromatic slot on H4Rime (blue) and the corresponding region for H1Rhis (orange). Imetit and histamine are shown as magenta and cyan sticks. Residues comprising the pocket for H4Rime are indicated by sticks and for H1Rhis are shown as sticks and transparent spheres. d Sequence alignment of residues important for agonist binding in the histamine receptor family. Red triangles indicate residues corresponding to the aromatic slots in H4R. e, f TGFα shedding assay results of WT H4R and H4R mutants activated by histamine and imetit. The activities of the agonists are identified as pEC50 (e). Average Emax values were determined from the “log (agonist) vs. response -variable slope (three or four parameters)” function in GraphPad Prism 9 software (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA) (f). Data represent the mean ± SEM from n = 3 biologically independent experiments performed in triplicate. ND, not detected.