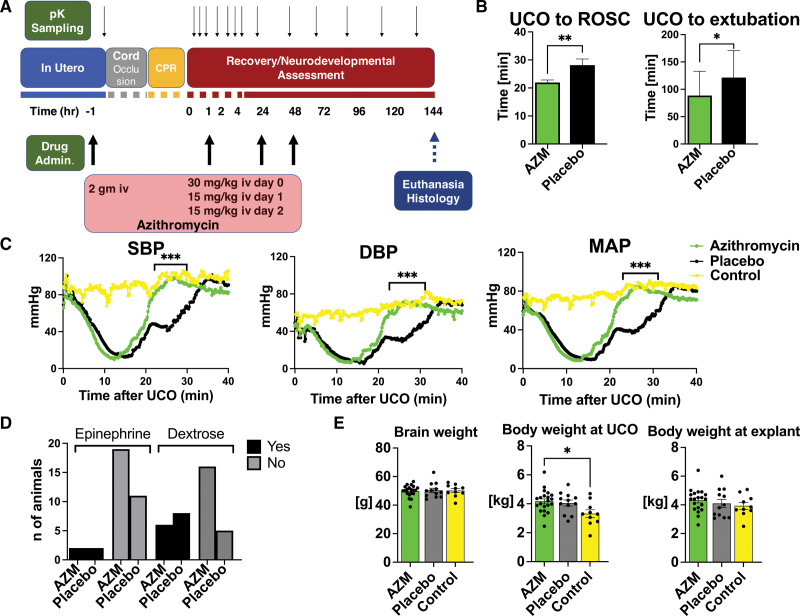
Figure 1.
Umbilical cord occlusion (UCO) model and resuscitation outcomes. A, Timeline of azithromycin (AZM) administration. B, Return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) was faster in AZM-treated animals, and the time to extubation was shorter compared with the placebo group. Groups were compared using unpaired t test for ROSC assessment and Mann-Whitney U test for extubation time. AZM: n=21, placebo: n=13. C, UCO (time 0 min) induced asystole with corresponding loss in cardiac output and hypotension. ROSC restored blood pressure to levels similar to age-matched controls. Hemodynamic data were analyzed using grouped analysis of the individual group’s means for a specific time point. AZM: n=18; placebo: n=13; control: n=6 (controls data were used with permission from Mike et al23). D, The incidence of second dose of epinephrine and dextrose administration was similar between the groups. The proportion of variables was assessed using Fisher exact test. AZM: n=21; placebo: n=13. E, There were no differences in selected anthropometric parameters between AZM and placebo. Brain and body weight differences were assessed using ANOVA. AZM: n=21; placebo: n=12; control: n=10. Data shown in the graphs B and E as mean±SEM, graph C are shown as mean, graph D is a contingency table. AZM-treated group, green. Placebo, black. Controls, yellow. CPR indicates cardiopulmonary resuscitation; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; MAP, mean arterial pressure; pK, pharmacokinetic; and SBP, systolic blood pressure. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.