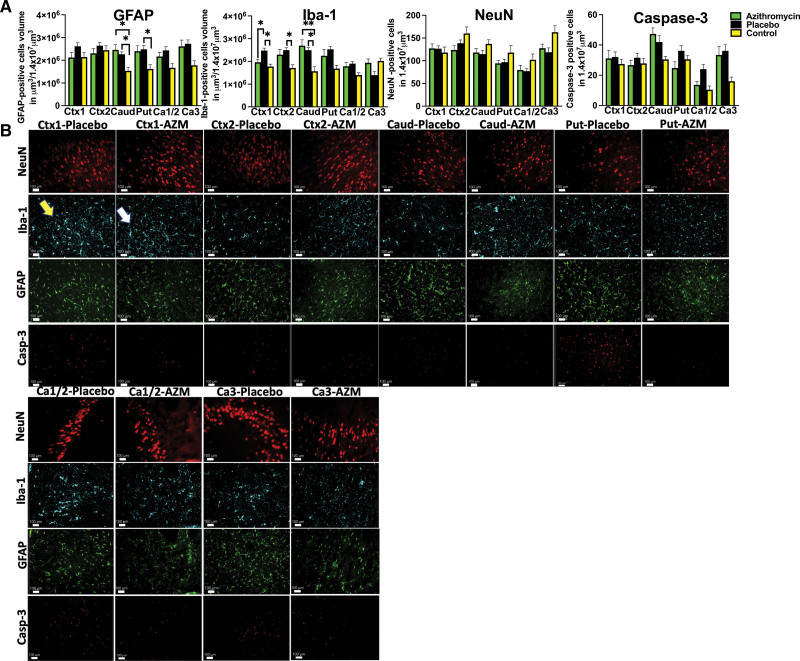
Figure 4.
Histological changes in gray matter. A, We compared quantitative changes in inflammatory markers of gliosis (GFAP [glial fibrillary acidic protein]) and microglial accumulation (Iba-1 [ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule-1]); neuronal counts (neuronal nuclei [NeuN]), cellular death markers (Casp-3 [caspase-3]) in cingulate gyrus (Ctx1), first parasagittal gyrus (Ctx2), caudate (Caud), putamen (Put), and Ca1/2 and Ca3 of the hippocampus. Analyzed were azithromycin (AZM): n=7 to 20, placebo: n=6 to 11, controls: n=5 to 8 (control data were used with permission from Mike et al23) using either ANOVA or Kruskal-Wallis test. Data are presented as mean±SEM. Brackets show significance as follows: *P<0.05, **P<0.01. AZM-treated animals (green) vs placebo (black) vs control (yellow). B, The observed quantitative changes are represented in photomicrographs by accumulation of microglial cells in Ctx-1 (Iba-1 marker), thickened glial cells in Caud in both groups, and Put in the placebo group (GFAP). Placebo animal histologies (yellow arrow) are compared with the AZM-treated animals (white arrow).