Fig. 2.
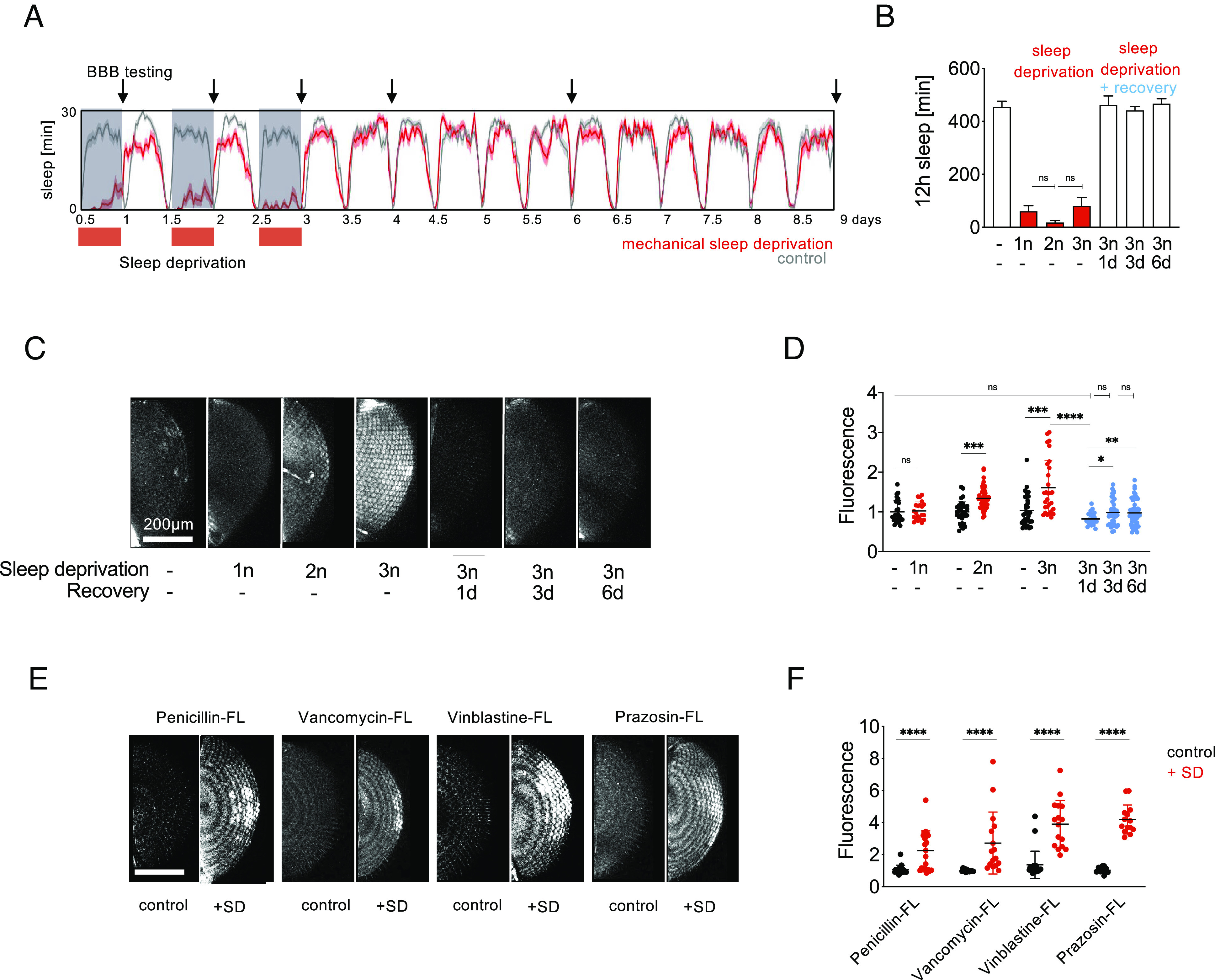
Mechanical SD reversibly increases BBB permeability and improves drug penetration into the brain. (A) Sleep plot for mechanical SD. Wild-type flies were sleep deprived using a custom-built machine by randomized shaking for 2x2 s every 5 m for 1, 2, or 3 subsequent nights (n) during their normal sleep time between ZT 12–24, plotted in red, and left to recover for up to 6 d. Average sleep in 16 flies is shown, binned as sleep in 30 min. Arrows denote timepoints of BBB testing shown in (C). (B) Quantification of sleep data in (A). Shown is total sleep in 12 h prior to injection for each group. n = 16. Statistical significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA with Dunn’s post hoc testing. Red, sleep-deprived flies. —| indicates comparison to 1n SD. (C) Flies were sleep deprived as shown in (A) and injected with 10 kDa Dextran-TexasRed to assess BBB permeability after 1, 2, or 3 nights of SD or let to recover sleep for 1, 3, or 6 d prior to BBB testing. (D) Quantification of BBB permeability in (C). n = 30 to 40. Red, sleep-deprived flies; blue, flies after recovery sleep; black, controls. Statistical significance was calculated using t tests for pairwise and one-way ANOVA with Dunn’s post hoc testing for multiple comparisons. —| indicates comparisons to non-sleep-deprived flies. (E) Three nights of SD increase BBB penetration of fluorescein-labeled penicillin, vancomycin, vinblastine, and prazosin. Flies were mechanically sleep deprived or left to sleep during Zeitgeber time 12 to 24 h for three consecutive nights and injected with fluorescently labeled bioactive drugs the next morning for BBB assessment. (F) Quantification of BBB permeability in (E). n = 30 to 40. Red, sleep-deprived flies; black, controls. For quantification of BBB permeability, fluorescence was measured for both eyes of each fly. Each dot represents normalized fluorescence in one eye. Statistical significance was calculated using t tests. Significance levels are P < 0.05: *, <0.01: **, <0.001: ***, <0.0001: **. SD: sleep deprivation.
