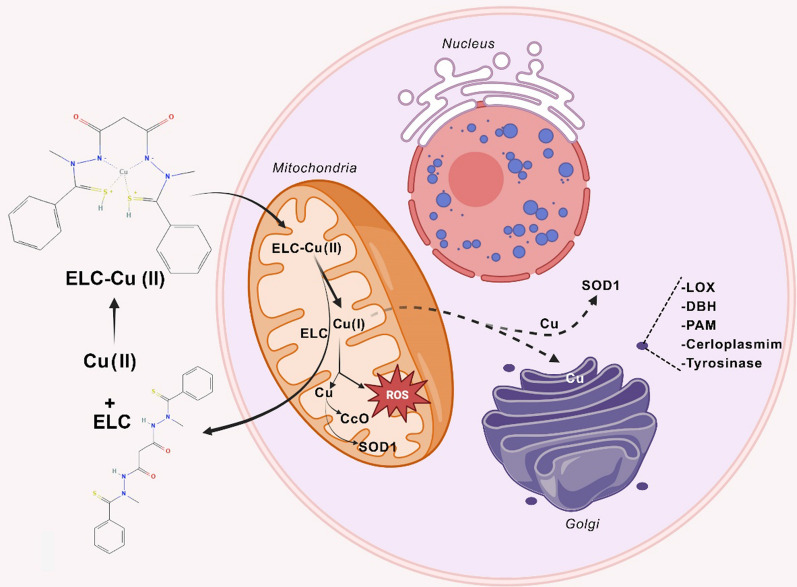
Fig. 4.
Copper delivery into the cell by ELC. In the extracellular environment, ELC binds copper (Cu2+) and transports it into mitochondria. Ferredoxin 1 (FDX1) is likely responsible for reducing the ELC-Cu(II) complex in the mitochondrial matrix into ELC and Cu(I). Reactive oxygen species (ROS) can be generated as a result of the release of Cu(I). The metalation of cytochrome c oxidase (CcO) with copper(I) has been demonstrated to be bioavailable. Other subcellular compartments may also receive copper(I) for use in cuproenzyme maturation. Including superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) in the mitochondria and cytosol and lysyl oxidase (LOX), dopamine β-hydroxylase (DBH), ceruloplasmin, peptidylglycine α [1] amidating monooxygenase (PAM), and tyrosinase in the secretory pathway