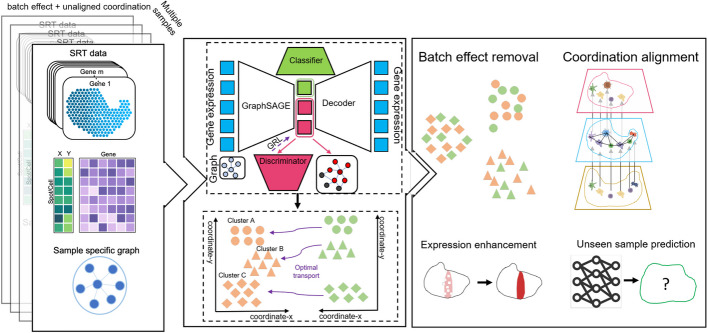
Fig. 1.
Overview of SPIRAL. SPIRAL includes two consecutive modules: SPIRAL-integration (upper right) and SPIRAL-alignment (bottom right). SPIRAL-integration takes combined gene expressions and separated graphs, constructed by spatial coordinates of spots for each sample, as input and learns the disentangled embeddings as biological embeddings and noise embeddings via a discriminator and a classifier. SPIRAL tries to preserve the spatial structures on biological embeddings and to preserve the expression patterns on the whole embeddings. SPIRAL-alignment takes cluster annotations of SPIRAL-integration and spatial coordinates as input to align coordinates of shared clusters between reference and query samples via Gromov-Wasserstein optimal transport. Through SPIRAL, the corrected embeddings, gene expressions, and aligned coordinates can be obtained. SPIRAL also can predict cluster labels and new coordinates for new SRT data