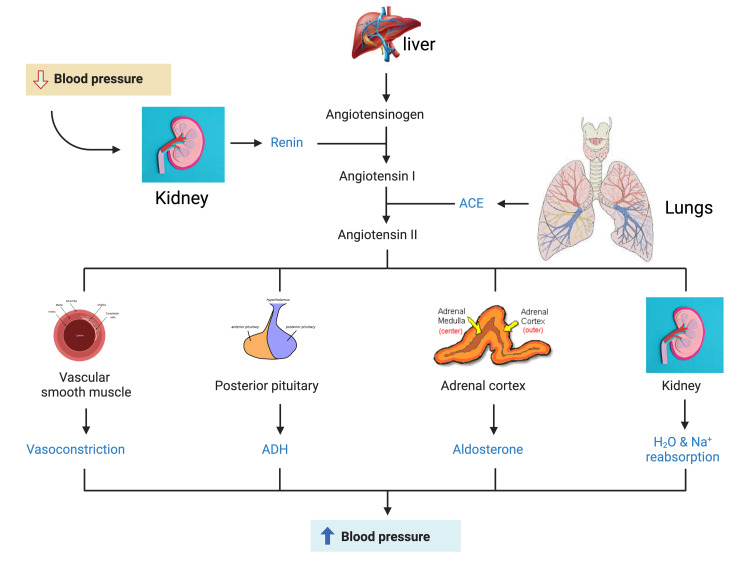
Figure 2. Schematic representation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system activation in response to a reduction in blood pressure.
The kidneys release renin, which converts angiotensinogen, released by the liver, to angiotensin I. The lungs release angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), which converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II. Angiotensin II, in turn, stimulates peripheral vasoconstriction, the posterior pituitary to release antidiuretic hormone (ADH), the adrenal cortex to release aldosterone, and the kidneys to increase water and sodium reabsorption. The result is a reactive increase in blood pressure.
Created by BioRender.com.