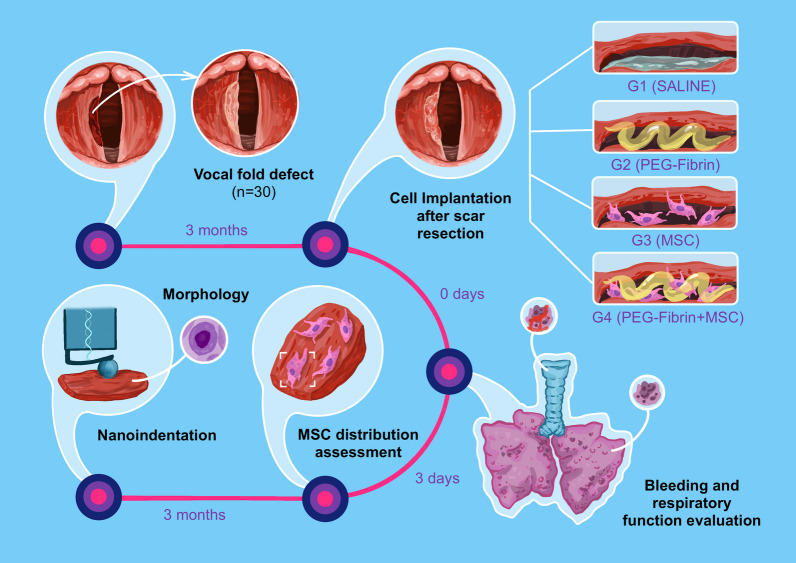
Fig. 1.
Experimental design. As tested agents, we chose a hydrogel system based on PEG-fibrin conjugates and a bioequivalent containing, beside the hydrogel, human bone marrow-derived MSC. The implantation was performed in the heterotopic (subcutaneously to rats) and orthotopic (secondary wound after the scar excision in rabbits) positions. In the first case, the animals were removed from the experiment on days 3 and 7, and a histological study was performed. In the second case, the VF scar was first modeled, it formed during 3 months, then, upon its excision, the cell-laden hydrogel system was administered, and the surgery efficiency was estimated 3 months later by means of histological and mechanical studies. The effects of the administered agents on the hemorrhage and breathing function were additionally studied, and the cells’ distribution in tissues was tracked depending on the used carriers. The figure is originally created by the authors