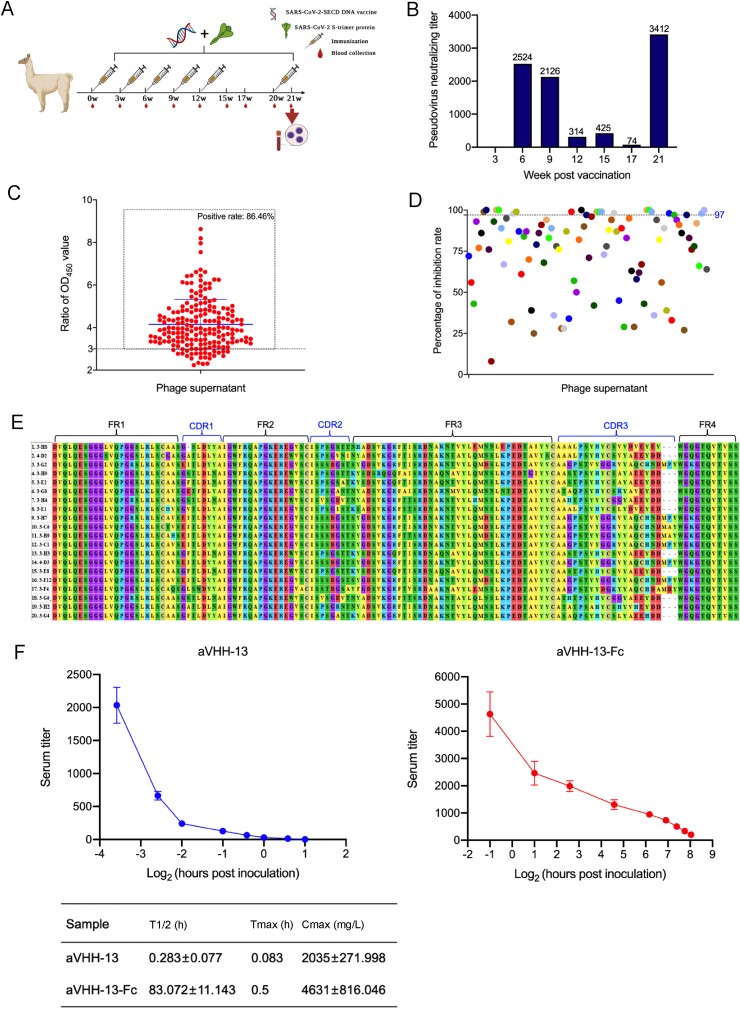
Fig. 1.
Screening and characterization of SARS-CoV-2 nanobodies (Nbs). A Alpacas were immunized with SARS-CoV-2 S DNA vaccine and S-trimer protein for 6 doses at week 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, and 20, respectively. B Neutralizing titers of immunized alpaca serum was detected by SARS-CoV-2 D614G pseudovirus based on HIV pseudovirus system following vaccination. PBMCs were isolated from the whole blood of alpacas on week 21 for construction of phage library. C Positive rate of 192 monoclonal phage supernatants by phage-ELISA, the positive sample was defined as the ratio of OD450 value between the experiment group and negative control is greater than 3. D Percentage of inhibition of 192 monoclonal phage supernatants to SARS-CoV-2 D614G pseudovirus. According to the capture of luciferase report gene, Nbs with inhibition rates greater than or equal to 97% were extracted for sequencing and alignment. E Sequence alignment of 20 VHH gene sequences. FR1 to FR4 and CDR1 to CDR3 were marked. F Metabolic dynamics of Nbs. Antibody level of aVHH-13 and aVHH-13-Fc were measured at different time points post tail vein injection in mice. T1/2: the half-life of terminal elimination, the time required for the terminal phase blood drug concentration to decrease by half. Tmax: peak time, the time for the drug action to reach the peak. Cmax: peak concentration, the highest value of blood drug concentration after administration. Data were presented as mean with standard deviation.