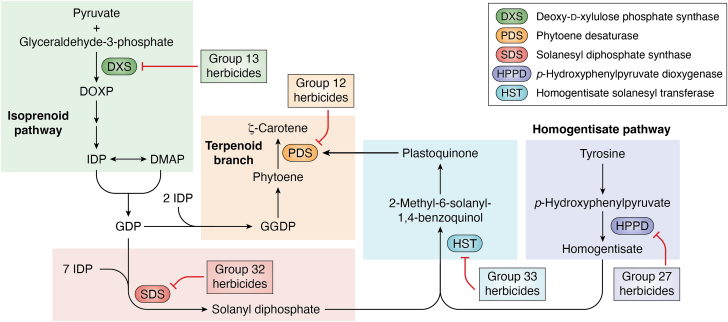
Figure 4.
Overview of herbicides inhibiting carotenoids and plastoquinone biosynthesis. The isoprenoid pathway (green box) begins with the formation of deoxy-d-xylulose phosphate (DOXP) by the action of DXS. This pathway ultimately leads to the formation of isopentenyl diphosphate (IDP). The condensation of IDP with dimethyl allyl diphosphate (DMAP) initiates the terpenoid branch (yellow box) that can be directed toward carotenoid biosynthesis, with PDS catalyzing a key step. Terpenoid biosynthesis can lead to the formation of solanesyl diphosphate (red box), the lipophilic tail of plastoquinone via the action of SDS. The benzoquinone head of plastoquinone is derived from the homogentisate pathway (purple box) involving the key enzyme HPPD. The complete plastoquinone structure is assembled by transferring the solanesyl tail to the homogentisate head (blue box) by the action of HST. The targets of herbicide groups affecting carotenoid and/or plastoquinone biosynthesis are included. DXS, deoxy-d-xylulose phosphate synthase; HPPD, hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase; HST, homogentisate solanesyltransferase; PDS, phytoene desaturase.