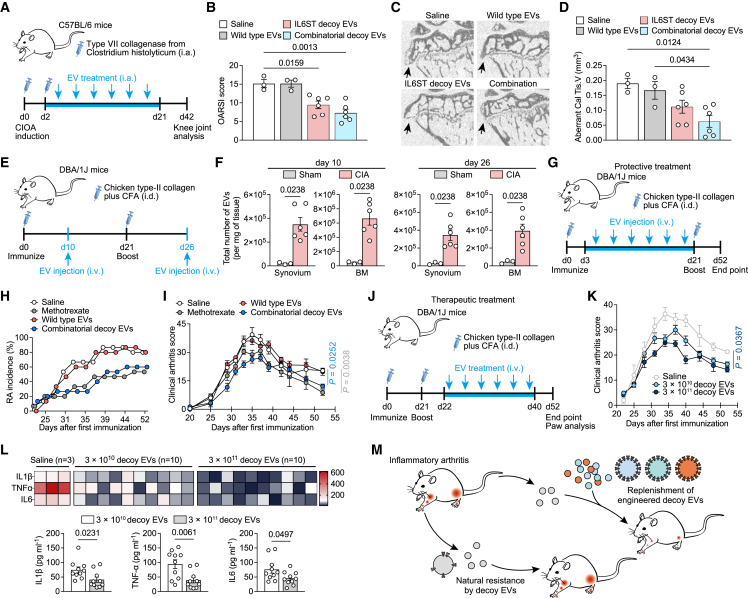
Figure 6.
Decoy EV treatment relieves disease phenotypes of several arthritis mouse models
(A) Experimental design for assessing effects of decoy EV treatment on knee OA progression using a CIOA mouse model.
(B) Clinical Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) score of disease progression in CIOA mice intraarticularly injected with saline (n = 3), 3 × 1011 wild-type EVs (n = 3), 3 × 1011 IL6ST decoy EVs (n = 6), or 3 × 1011 combinatorial decoy EVs (n = 6) at the endpoint (day 42). The combinatorial EVs were composed of IL6ST, TNFR1, and IL1RⅡ decoy EVs in equal proportions (1011 of each type).
(C and D) Representative micro-CT images of sagittal views of subchondral bone medial compartment (C) and quantification of aberrant calcified tissue volume (Cal Tis. V) (D) in CIOA mice treated with saline (n = 3), 3 × 1011 wild-type EVs (n = 3), 3 × 1011 IL6ST decoy EVs (n = 6), or 3 × 1011 combinatorial decoy EVs (n = 6) at the endpoint (day 42). Black arrows indicate osteophytes on the edge of the tibial plateau.
(E) Experimental design for assessing the biodistribution of decoy EVs in diseased tissues of a CIA mouse model. 5 × 1010 EVs were injected intravenously into mice in a single dose at day 10 or day 26, respectively. The distribution of decoy EVs in synovium and bone marrow was detected using NTA 6 h after EV injection.
(F) EV numbers in synovium and bone marrow from sham mice (n = 3) or CIA mice (n = 6) were measured using NTA.
(G) Experimental design for assessing the protective effects of decoy EVs on arthritis onset in a CIA mouse model. Mice were intravenously injected with saline, 2 mg/kg methotrexate, 3 × 1011 wild-type EVs, or 3 × 1011 combinatorial decoy EVs from day 3 to day 21 after the first immunization.
(H) The incidence of arthritis in (H) was observed and recorded from day 21 to the endpoint (day 52).
(I) Clinical arthritis score showing disease progression in CIA mice treated with saline (n = 3), 2 mg/kg methotrexate (n = 5), 3 × 1011 wild-type EVs (n = 5), or 3 × 1011 combinatorial decoy EVs (n = 12) over time.
(J) Experimental design for assessing the therapeutic potential of decoy EVs on arthritis symptoms in a CIA mouse model.
(K) Clinical arthritis score of disease progression in CIA mice treated with saline (n = 3), 3 × 1010 combinatorial decoy EVs (n = 10), or 3 × 1011 combinatorial decoy EVs (n = 10) over time. The combinatorial EVs were composed of IL6ST, TNFR1, and IL1RⅡ decoy EVs in equal proportions.
(L) Heatmap and quantification of serum IL1β, TNFα, and IL6 in CIA mice treated with saline (n = 3), 3 × 1010 decoy EVs (n = 10), or 3 × 1011 decoy EVs (n = 10). Saline treatment was used as a negative control. Cytokines were measured using Luminex assay.
(M) Schematic diagram showing proposed mechanism of action for therapeutic potential of decoy EVs in inflammatory arthritis.
All data are presented as mean ± SEM. In (B) and (D), statistical significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons. In (F) and (L), statistical significance was calculated using Student’s two-sided t test. In (I) and (K), statistical significance was calculated using two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test.