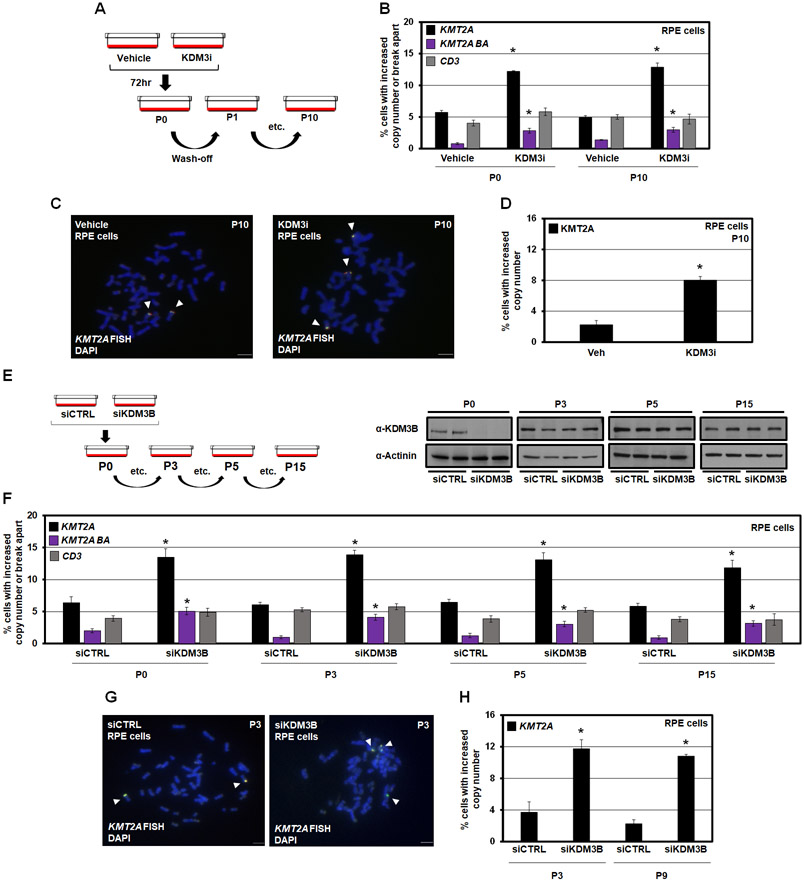
Figure 3. KDM3B suppression leads to integration and inheritance of KMT2A copy gains and break aparts.
(A) A KDM3i treatment schematic and associated passaging of RPE cells. Cells were treated with 25nM of KDM3i. Cells were passaged in media without KDM3i every 3 days for sequential passages.
(B) KMT2A and CD3 DNA FISH at passage 0 and passage 10 after KDM3i treatment, which demonstrates KMT2A copy gains and break aparts are inherited in RPE cells after 10 passages (P10). No significant change occurred with the CD3 probe.
(C) Example metaphase spreads for KMT2A FISH for Vehicle and KDM3i treated cells at passage 10. Arrowheads highlight the FISH signal.
(D) Quantification of the metaphase spreads with KMT2A FISH in KDM3i treated and passage 10 cells demonstrating increased copies of KMT2A are retained.
(E) A KDM3B siRNA schematic and associated passaging of RPE cells (left). Western blots for KDM3B at cell passages used for DNA FISH demonstrates KDM3B protein levels return to baseline by passage 3 (P3; right).
(F) KMT2A and CD3 FISH of KDM3B siRNA passaged cells demonstrates inheritance at passage 3, 5 and 15. No significant change occurred with the CD3 probe at any passage.
(G) Example metaphase spreads for KMT2A FISH for siCTRL and siKDM3B cells at passage 3. Arrowheads highlight the FISH signal.
(H) Quantification of the metaphase spreads with KMT2A FISH in cells treated with siCTRL and siKDM3B from two independently propagated siCTRL and siKDM3B cells at passages 3 and 9 demonstrating increased copies of KMT2A are retained.
Error bars represent the SEM. *p < 0.05 by two-tailed Student’s t-test. Scale bar represents 5μm.