Figure 3. Influence of cell type and CD1 transmembrane tethering on lipidomic outcomes.
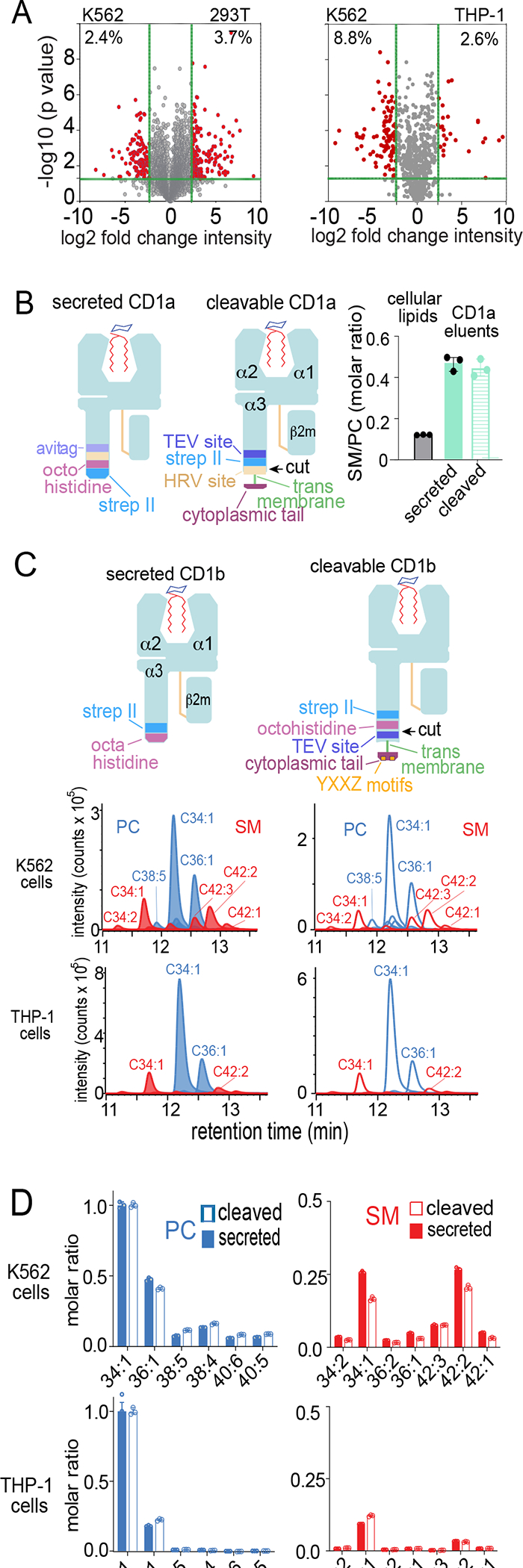
A) Total extracted lipids were compared to determine the percent lipidomic overlap by cell type. B) Cellular lipids were extracted in chloroform and methanol. CD1a proteins with a truncated transmembrane domain (secreted) were secreted into media. Transmembrane tethered CD1a was released into media by cleavage (cleaved) with human rhinovirus 3C protease. After captured with nickel or streptactin, CD1a-eluted lipids were subjected to MS analysis to detect SM/PC ratios, showing that CD1a captures a higher ratio compared to cellular lipids as reported previously.48 C) CD1b proteins with intact transmembrane and cytoplasmic tail sequences encoding a four-residue tyrosine containing (YXXZ) motif that directs endosomal recycling in THP-1 cells and K562 cells were released by TEV protease and captured with nickel and streptactin, following by elution of lipids analyzed in comparison to a mass normalized preparation of secreted CD1b proteins. Eluted PCs and SMs (length: saturation) were detected as ion chromatograms (C) and quantitated in by determining replicate chromogram areas (D). Results in (A-D) are representative of two experiments in each indicated cell type.
