Figure 4. Intrinsic IFNγ/STAT1 signaling is required for the differentiation of lung-BRMs.
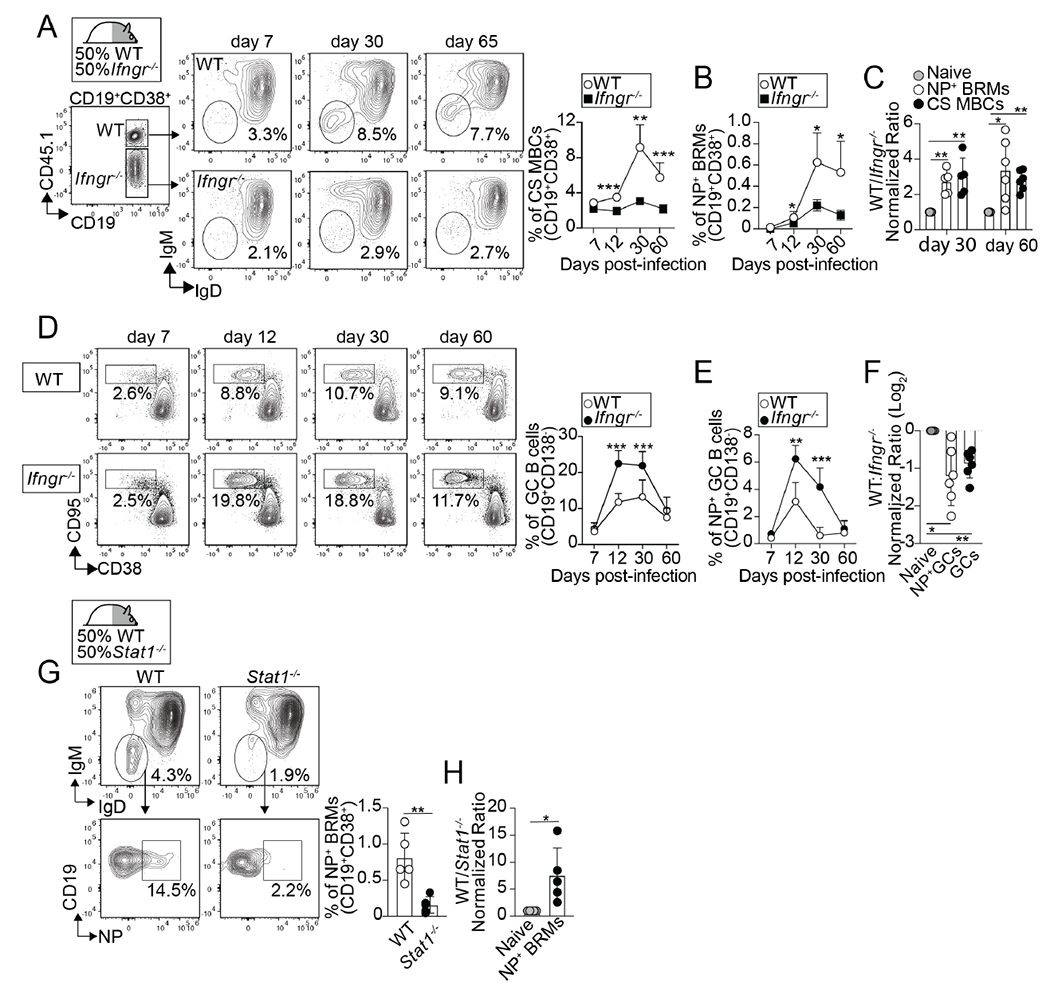
(A-F) WT/IfngR1−/− BM chimeras were infected with PR8. Frequency of class-switched memory B cells (A) and NP-specific lung BRMs (B) within the B6 and IfngR1−/− compartments in the lungs. P values were determined using a two-tailed Student´s t-test. (C) Ratio of B6 to IfngR1−/− naïve B cells (naïve), class-switched memory B cells (CS MBCs), and NP-specific BRMs. P values were determined by one-way ANOVA with a post-hoc Kruskal–Wallis comparison test. Frequency of total (D) and NP-specific GC B cells (E) within the B6 and IfngR1−/− compartments in the med-LN. P values were determined using a two-tailed Student´s t-test. (F) Ratio of B6 to IfngR1−/− naïve B cells, total GC B cells, and NP-specific GC B cells. P values were determined by one-way ANOVA with a post-hoc Kruskal–Wallis comparison test. Data are representative of three independent experiments (n=5-6 mice). (G-H) WT/ Stat1−/− BM chimeras were infected with PR8 and B cells from the lungs were analyzed on day 50.(G) Frequencies of NP-specific BRMs within the B6 and Stat1−/− compartments. Ratio of B6 to Stat1−/− naïve B cells and NP-specific BRMs. Data are representative of three independent experiments (n=5 mice). P values were determined using a two-tailed Student´s t-test.
