Figure 1. Fibrinogen structure.
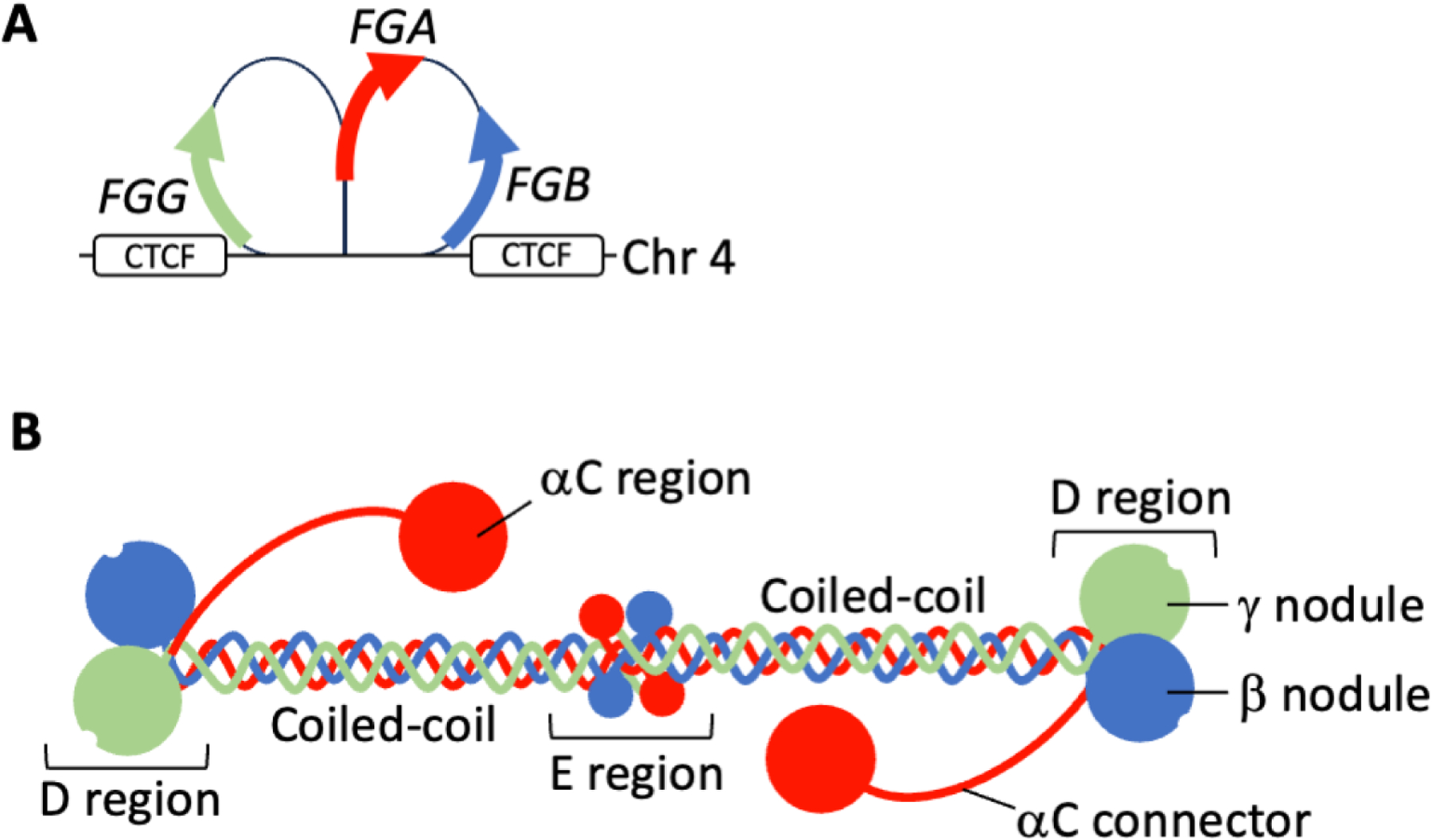
A) Fibrinogen is encoded by 3 genes (FGA, FGB, and FGG) clustered within a 65 kilobase region on human chromosome 4 (4q23-q32). FGA and FGG are in opposite orientation to FGB on the chromosome. CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) interaction sites flank the fibrinogen gene cluster direct chromatin looping and enable coordinate transcription of the fibrinogen genes. B) Fibrinogen is a 340-kDa hexameric glycoprotein containing 2 each of 3 polypeptide chains: Aα (red), Bβ (blue), and γ (green). The 6 fibrinogen polypeptides are arranged with N-termini in a central E region and C-termini radiating outwards with bilateral symmetry.
