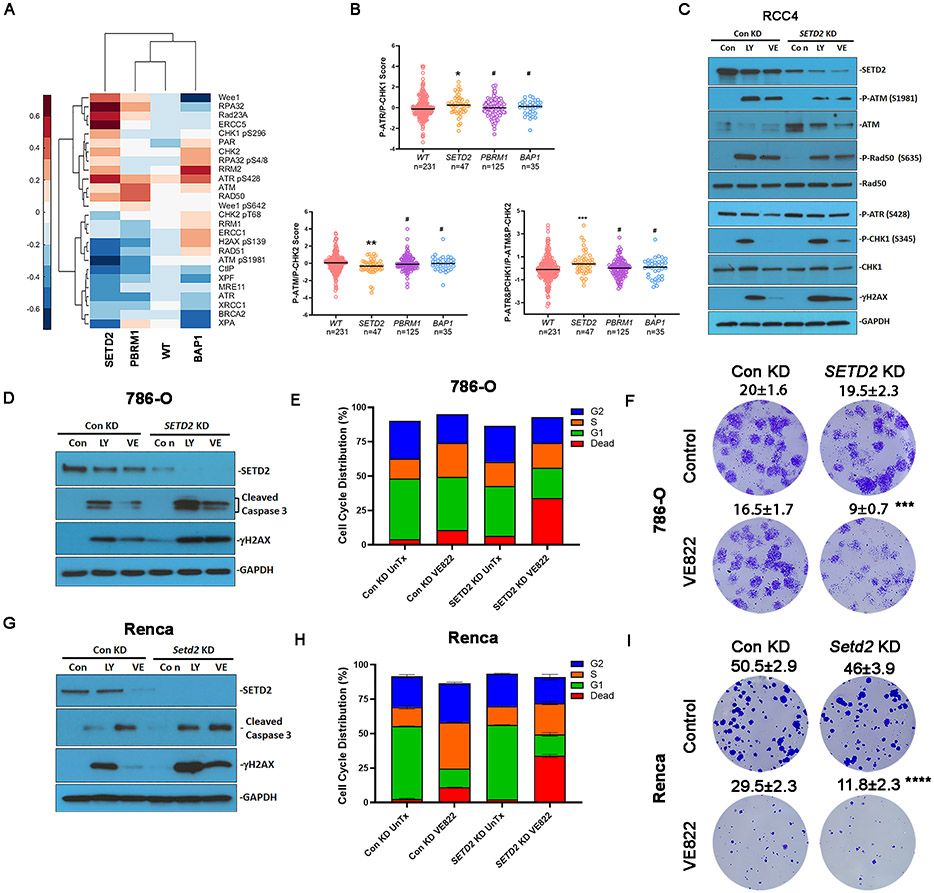
Fig. 2.
SETD2 loss was associated with preferential ATR activation and vulnerability to ATR inhibition. (A) Heatmap showing clustering of DDR proteins based on the mutational status of tumors in TCGA KIRC. Each column represents the average value for tumors with respective mutations or wild type (WT) for PBRM1, SETD2, and BAP1. (B) RPPA activation scores for P-ATR&P-CHK1 signaling, P-ATM&P-CHK2 signaling, or ratio of P-ATR&P-CHK1 to P-ATM&P-CHK2 signaling. Rank-sum test. (C) SETD2 knockdown influenced ATM and ATR signaling in response to LY2603618 or VE822. RCC4 cells expressing control shRNA or SETD2 shRNA were treated with 25nM LY2603618 or 2.5μM VE822 for 48 hrs. Protein expression was analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies against SETD2, P-ATM, ATM, P-Rad50, Rad50, P-ATR, P-CHK1, CHK1, γH2AX, and GAPDH. (D, G) SETD2 or Setd2 knockdown increased caspase 3 cleavage in response to LY2603618 and VE822 in (D) 786-O cells and (G) Renca cells. Protein expression was analyzed by immunoblot using antibodies against SETD2, cleaved caspase 3, γH2AX, and GAPDH. (E, H) SETD2/Setd2 knockdown increased cell death in response to VE822 treatment in (E) 786-O cells and (H) Renca cells. 786-O cells and Renca cells were treated with or without 2.5 μM VE822 for 24 hrs. The cell cycle distribution results represent the combined results of two independent experiments. (F, I) SETD2/Setd2 knockdown reduced the clonogenicity of (F) 786-O cells and (I) Renca cells. 786-O cells and Renca cells were treated with or without 50 nM VE822 for 5 days. Data represeFnt mean ± s.d., n= 4. ***P<0.001, and ****P<0.0001. Compared with control knockdown treated with VE822. Unpaired t test.