Fig. 2. MKLP1 and Arc are important for PolyA localization or translation at the MB.
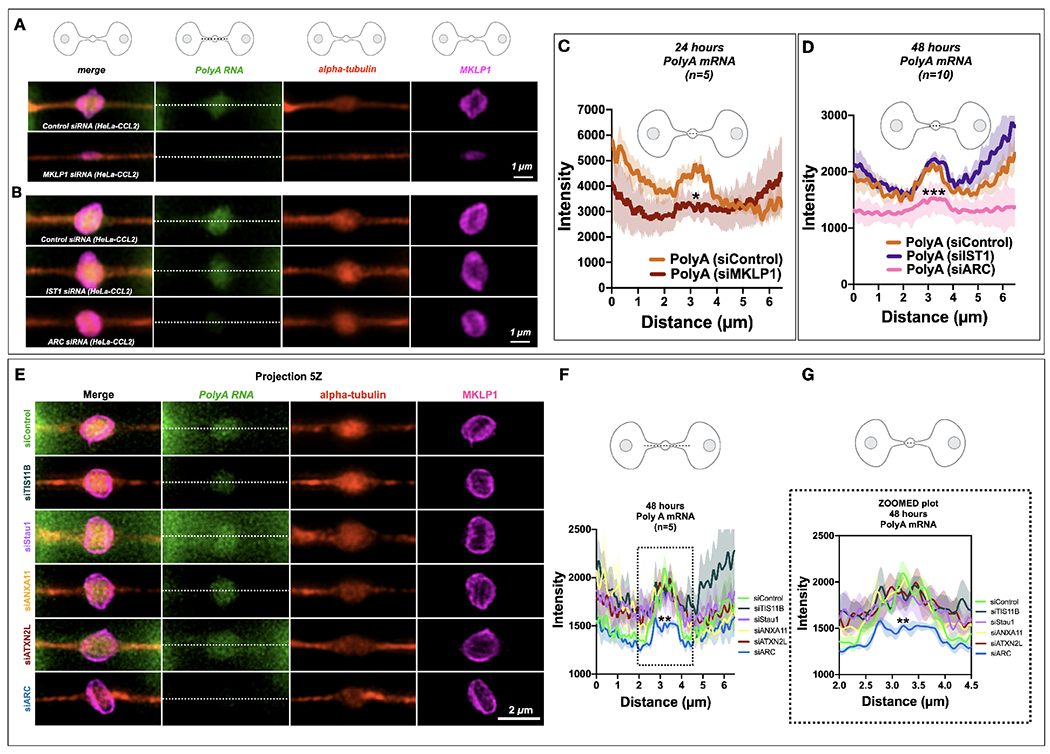
(A-B) PolyA signals (green) localized to the MB matrix surrounded by MKLP1 signal (magenta) in HeLa cells. RNAscope fixation techniques led to loss of the MB dark zone as seen by the tubulin bulge along the intercellular canal (red). Scale bars are 1 μm unless noted.
(C) Quantification of the line scans revealed that loss of MKLP1 by siRNA knockdown led to a decrease in polyA mRNA in MKLP1 siRNA-treated cells. *denotes significance
(D) Loss of ESCRT-III/IST1 did not affect RNA levels, but loss of ARC led to decreased levels of polyA mRNA in the MB. *denotes significance
(E-G) The RBP Arc leads to a decrease of PolyA RNA localization or maintenance at the MB, whereas loss of TIS11B, Stau1, ANXA11 or ATXN2L do not lead to a decrease in PolyA RNA signal. Note there is a slight insignificant decrease in siTIS11B treated cells. (F-G) Line scans across the bridge are shown (F) and a zoomed portion (G)(dotted line) shows the area of the dark zone. *denotes significance
