Figure 1. Femtosecond laser microdissection (fs-LM) method for the isolation and collection of single arrested meiosis I oocytes at different ages for scRNA seq.
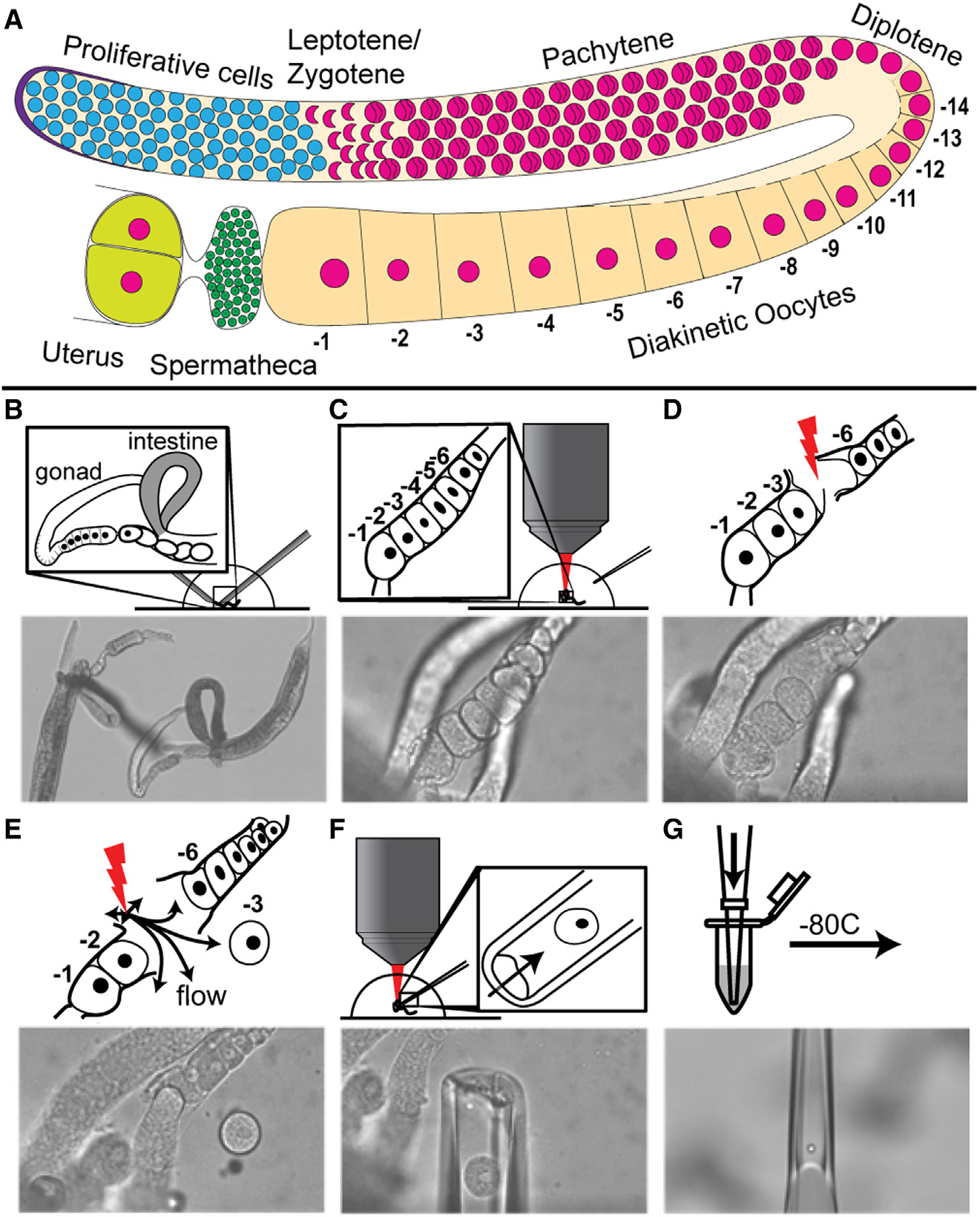
(A) Drawing of one C. elegans hermaphroditic germline arm with major cell populations labeled. (B–G) The fs-LM method16 involves the following steps. (B) Sever the animal at the pharynx with two 28G needles by hand under a stereoscope to expose the gonad and part of the uterus. (C) Transfer the buffer droplet containing the dissected animals to an upright microscope equipped with the fs-LM setup and a micropipetting system. (D) Ablate non-target oocytes (−4 and −5) closest to the target oocyte (−3) to create a passage for releasing the target oocyte. (E) Dislodge the target oocyte and move it away from the carcass by creating gentle water jets with low-energy off-target fs-laser pulses. (F) Extract the released target oocyte with a glass micropipette. (G) Deposit the collected single oocyte into the lysis buffer and freeze at −80°C. See also Figure S1.
