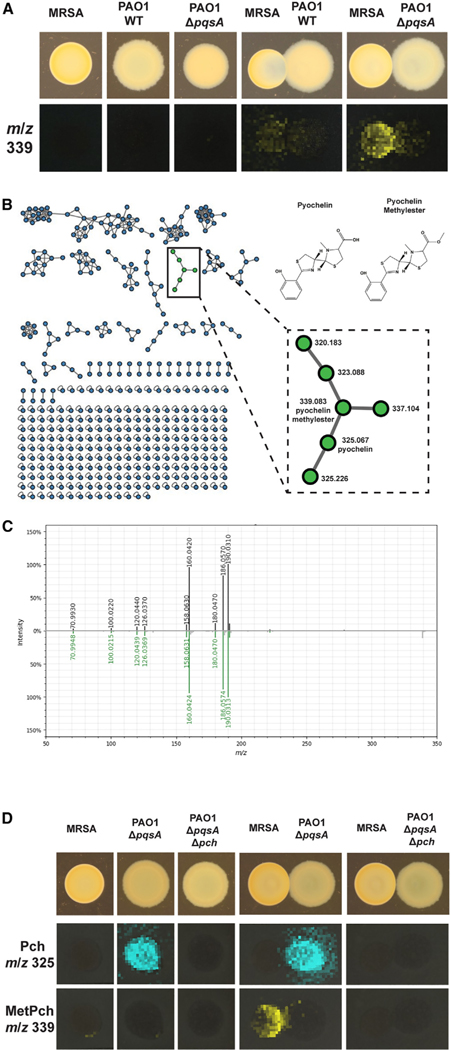
Figure 1. Pyochelin methyl ester (MetPch) is produced during interaction of S. aureus and P. aeruginosa.
(A) MALDI-MSI of S. aureus and P. aeruginosa grown as mono-cultures or interactions. Photographs of the cultures are shown on top. P. aeruginosa wild type (PAO1 WT), but not a P. aeruginosa quinolone mutant (PAO1 ΔpqsA), inhibits S. aureus WT (MRSA) when grown in co-culture. The bottom row shows the false colored m/z distribution of an unknown compound with m/z 339 that was exclusively observed during interaction of P. aeruginosa and S. aureus.
(B) The interaction specific compound (m/z 339) is annotated as MetPch, a member of the Pch molecular family, by molecular networking.
(C) Mirror plot comparing the MS2 spectrum of isolated MetPch (top; black trace) with its GNPS library match (bottom; green trace).
(D) MALDI-MSI of S. aureus and P. aeruginosa producing (ΔpqsA) or not producing Pch (ΔpqsA Δpch). Photographs of the cultures are shown on top. The middle row shows the false colored m/z distribution for Pch (m/z 325) and the bottom row for MetPch (m/z 339). Pch production can be observed by PAO1 ΔpqsA but not PAO1 ΔpqsA Δpch.