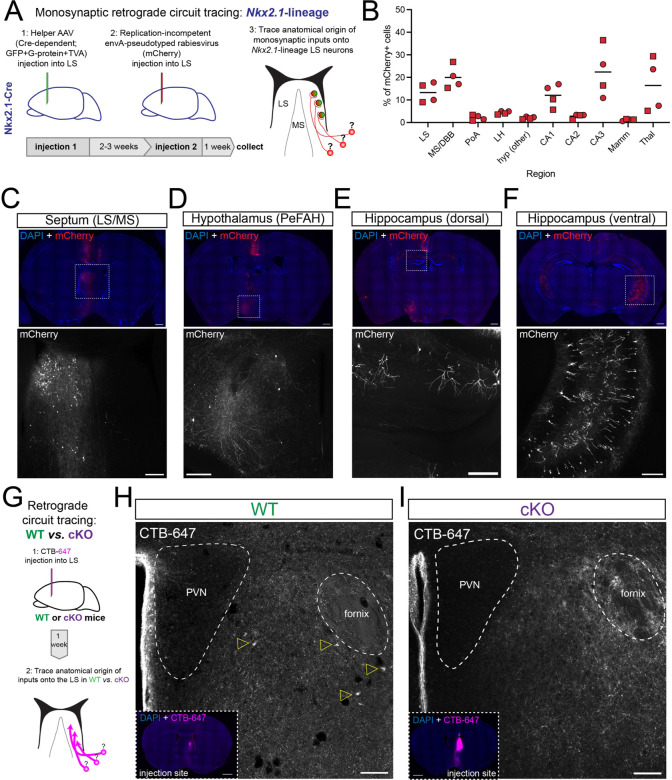
Figure 3: Disrupted PeFAH to lateral septum connectivity in cKO mice.
A) Cartoon illustrating the experimental approach for retrograde monosynaptic circuit tracing from Nkx2.1-lineage neurons in the lateral septum. B) Graph summarizing the distribution of retrogradely labeled cells (represented as % of total mCherry+ cells) in the 10 main sources of synaptic inputs onto LS Nkx2.1-lineage cells. Squares represent male mice (n = 2), and circles female mice (n = 2). LS: lateral septum; MS/DBB: medial septum/diagonal band of Broca; PoA: preoptic area; LH: lateral hypothalamus; hyp: hypothalamus; CA1/2/3: Cornus Ammonis 1/2/3 regions of the hippocampus; Mamm: mammillary region; Thal: thalamus. C-F) Example images of retrogradely labeled neurons in different areas of the brain of an Nkx2.1-Cre mouse subjected to retrograde monosynaptic circuit tracing. The top panels show overview images stained for mCherry (red; expressed by neurons synapsing onto Nkx2.1-lineage cells in the LS) and counterstained with DAPI (blue); bottom panels show a closeup view of the areas highlighted by white dashed boxes in the overviews, displaying the mCherry channel (gray). The regions highlighted are: C) septum (lateral and medial); D) hypothalamus (PeFAH, perifornical area of the anterior hypothalamus); E) CA1 area in the rostro-dorsal hippocampus; F) CA1/CA3 area in the caudo-ventral hippocampus. Scale bars, 500 μm (overviews), 250 μm (closeups). G) Cartoon illustrating the experimental approach for retrograde circuit tracing in WT and cKO mice. CTB-647, cholera toxin beta subunit conjugated to Alexa-647 fluorophore. H) Representative image of the PeFAH of a WT mouse subjected to retrograde circuit tracing. Empty yellow arrowheads indicate the cell bodies of neurons labeled with CTB-647 injected into the LS (inset: injection site). PVN, periventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. I) Representative image of the PeFAH of a cKO mouse subjected to retrograde circuit tracing (inset: injection site). Note the absence of CTB-647-labeled cell bodies. PVN, periventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. Scale bars for H and I, 100 μm (main images), 500 μm (insets).