Fig. 4. Overexpression of FGF21 in transgenic mice suppresses alcohol-mediated induction of SRPK2 and protects against the progression of ALD.
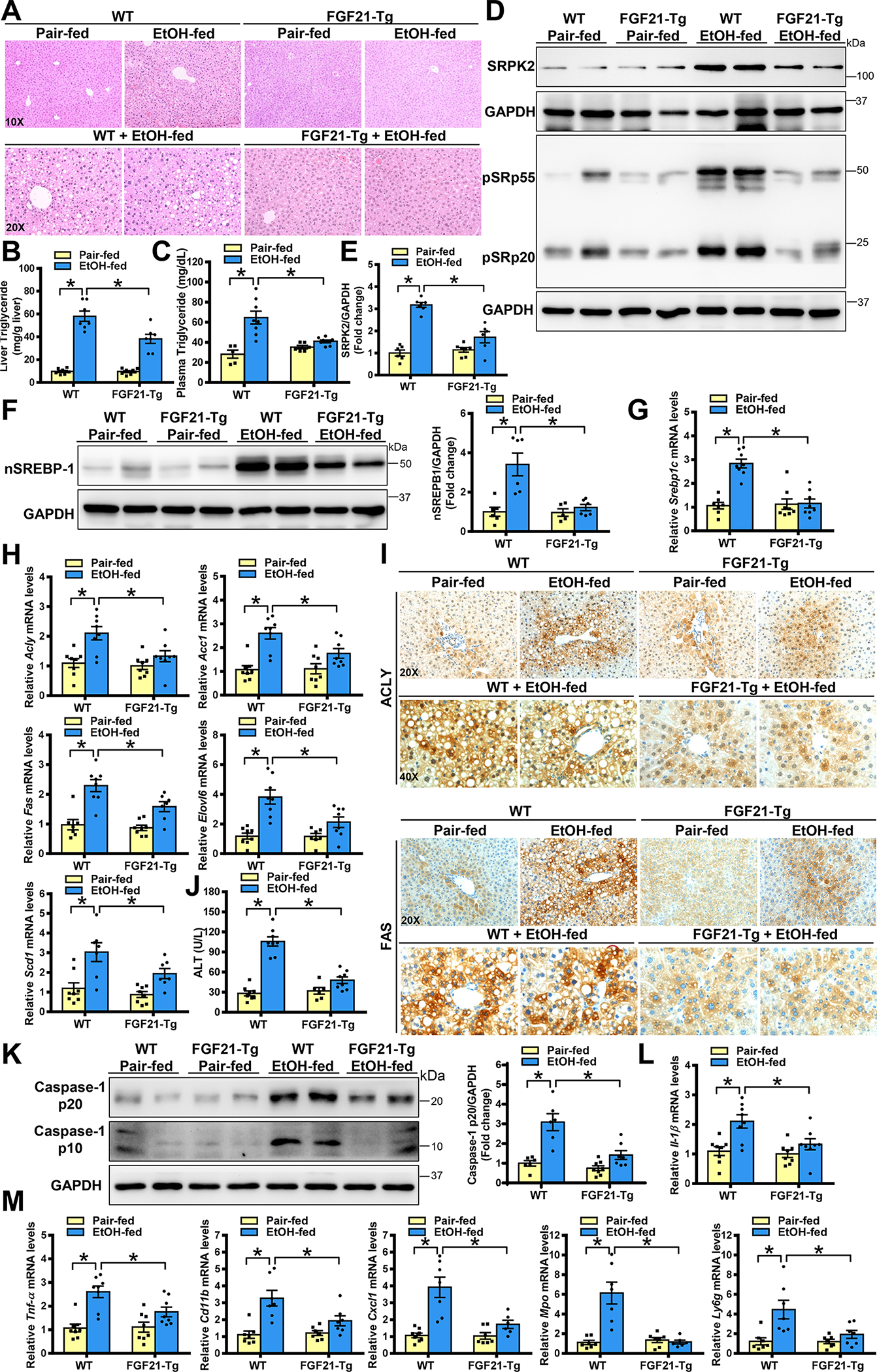
WT mice and FGF21 overexpression in transgenic (FGF21-Tg) mice were subjected to a Lieber-DeCarli alcohol liquid diet for 10 days plus one binge alcohol feeding at the end of experiments, or a pair-fed control diet. All mice were sacrificed 9 hours post-binge.
A. Representative H&E staining of live sections in WT and FGF21-Tg mice.
B-C. Hepatic and plasma triglyceride concentrations were lowered in FGF21-Tg mice after chronic-binge alcohol feeding.
D-F. Immunoblots and densitometric quantification for SRPK2, phosphorylation of SR proteins, and nSREBP-1.
G-H. Real-time qRT-PCR analysis of mRNA levels of SREBP-1 and its target lipogenic genes. FGF21-Tg mice exhibited much lower expression of lipogenic genes than that in WT mice after chronic-binge alcohol feeding.
I. Immunohistochemistry staining for ACLY and FAS. Notably, the number and distribution of ACLY+ and FAS+ hepatocytes were decreased in FGF21-Tg mice following chronic-binge alcohol feeding.
J. ALT assays to measure liver injury.
K. Immunoblots and densitometric quantification for p10 and p20 fragments of caspase-1.
L-M. Real-time qRT-PCR analysis showed that expression of pro-inflammatory regulators and mediators (IL-1β, TNF-α, Cdc11b, CXCL1, MPO, and Ly6g) was much lower in FGF21-Tg mice than in WT mice after chronic-binge alcohol feeding.
The data are presented as the mean ± S.E.M., n=6–8 per group. *P<0.05 between two groups.
Images were acquired using 20X and 40X objectives.
