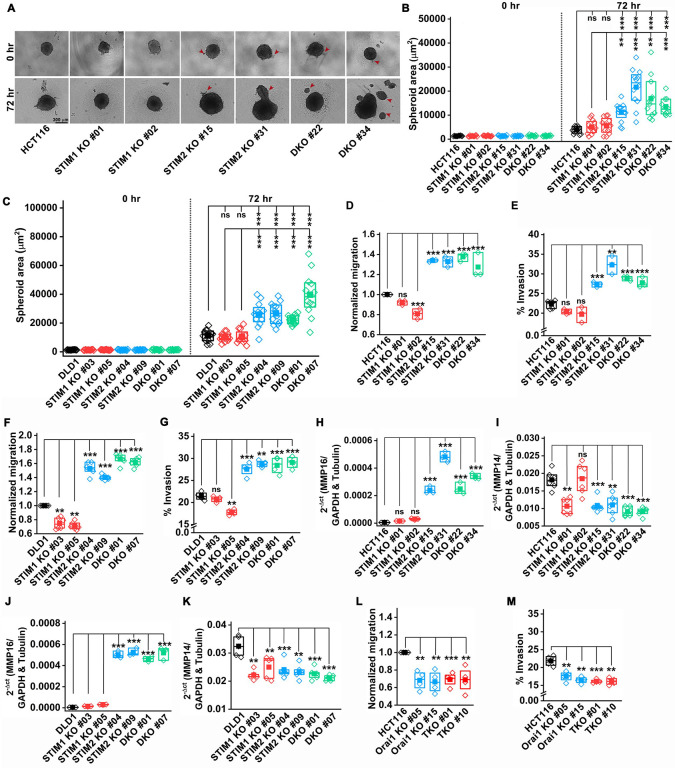
Figure 3. Loss of STIM2 enhances CRC proliferation and metastasis.
(A, B) Spheroid formation assay showing (A) representative image of spheroid formed by HCT116, and clones of STIM1 KO, STIM2 KO, and DKO in HCT116 cells, (B) quantification of the spheroid area at 0 and 72 hr. (Scale bar 300 μm)
(C) Quantification of the spheroid area of DLD1 and clones of STIM1 KO, STIM2 KO, and DKO in DLD1 cells.
(D, E) Quantification of (D) normalized migration and (E) percent invasion of HCT116 and clones of STIM1 KO, STIM2 KO, and DKO in HCT116 cells using Boyden chamber assay.
(F, G) Quantification of (F) normalized migration and (G) percent invasion of DLD1 and clones of STIM1 KO, STIM2 KO, and DKO in DLD1cells using Boyden chamber assay.
(H, I) RT-qPCR analysis of mRNA levels of (H) MMP16 and (I) MMP14 in HCT116, STIM1 KO, STIM2 KO, and DKO clones of HCT116 cells.
(J, K) RT-qPCR analysis of mRNA levels of (J) MMP16 and (K) MMP14 in DLD1 and clones of STIM1 KO, STIM2 KO, and DKO clones of DLD1 cells.
(L, M) Quantification of (L) normalized migration and (M) percent invasion of HCT116 and clones of Orai1 KO, and Orai TKO in HCT116 cells using Boyden chamber assay.
ANOVA followed with a post hoc Tukey test except for F-M where the paired t-test was used to compare between groups. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001