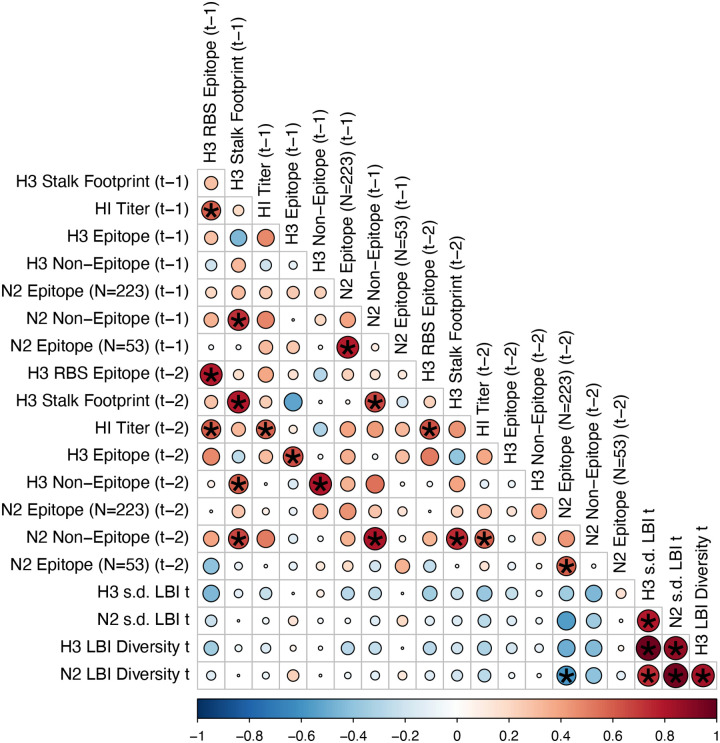
Figure 2 – figure supplement 6. Pairwise correlations between H3 and N2 evolutionary indicators (one- and two-season lags).
We measured Spearman’s rank correlations between seasonal measures of H3 and N2 evolution, including H3 RBS distance, H3 epitope distance, H3 non-epitope distance, H3 stalk footprint distance, HI log2 titer distance, N2 epitope distance based on 223 or 53 epitope sites, N2 non-epitope distance, and the standard deviation (s.d.) and Shannon diversity of H3 and N2 local branching index (LBI) values in the current season t. Seasonal distances were estimated as the mean distance between strains circulating in the current season t and those circulating in the prior season (t − 1) or two seasons ago (t − 2). The Benjamini and Hochberg method was used to adjust P-values for multiple testing. The color of each circle indicates the strength and direction of the association, from dark red (strong positive correlation) to dark blue (strong negative correlation). Stars within circles indicate statistical significance (adjusted P < 0.05).