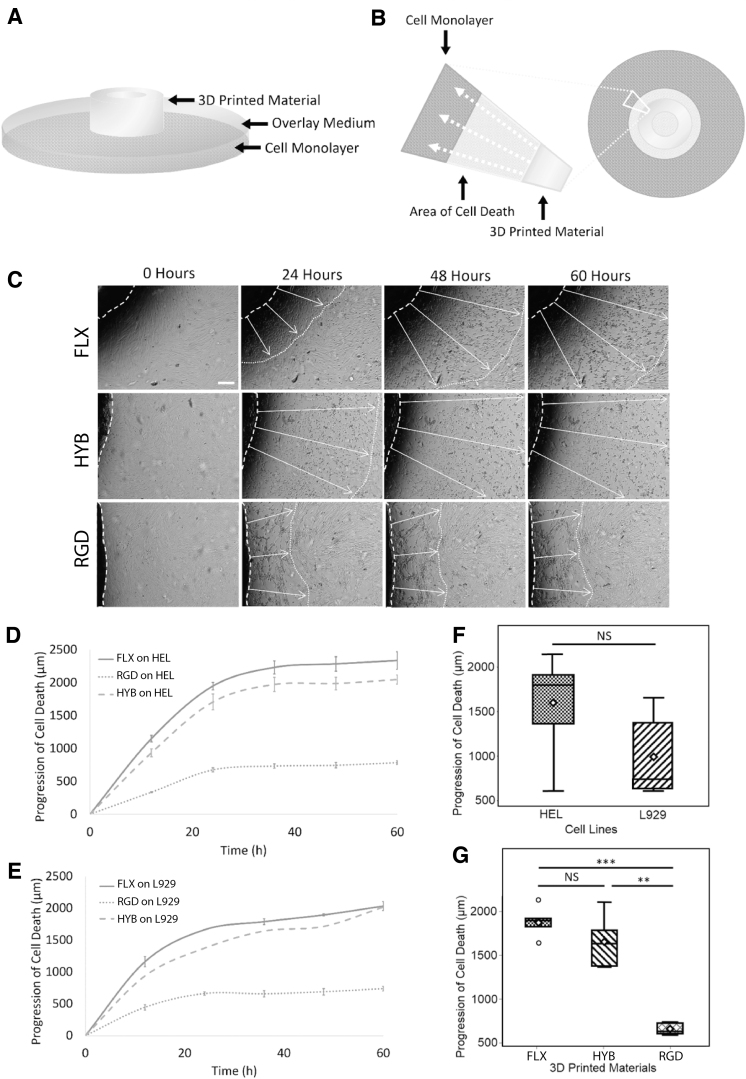
FIG. 2.
Cytotoxicity test of untreated (raw) materials. (A) Assay setup. A methylcellulose overlay media acted as a cushion between the test material and the cell monolayer. (B) Schematics of an area of cell death. Cytotoxins created an area of cell death around the test material as they diffused through the overlay medium in the direction of white arrows. (C) Representative time-lapse images. The progression of cell death spread from the material outward, shown in time-lapse images as white arrows. Scale bar: 250 μm. (D) HEL cell death as a function of time. On the human fibroblast cell line (HEL), the death progression curves showed that the FLX and HYB materials were more cytotoxic than the RGD material. (E) L929 cell death as a function of time. A mouse fibroblasts cell-line (L929) was also used in a second assay, which showed similar trends seen in the HEL cells. Both cell lines' death was slowed down after hour 36. (F) Overall cytotoxicity for both the cell lines showed at hour 36; the human fibroblasts were more sensitive to the materials' cytotoxicity, although insignificant. (G) Collective cytotoxicity of all three materials at hour 36 showed that RGD was significantly less toxic than FLX materials (FLX and MIX). Three samples were recorded in eight different locations each for D–G results.