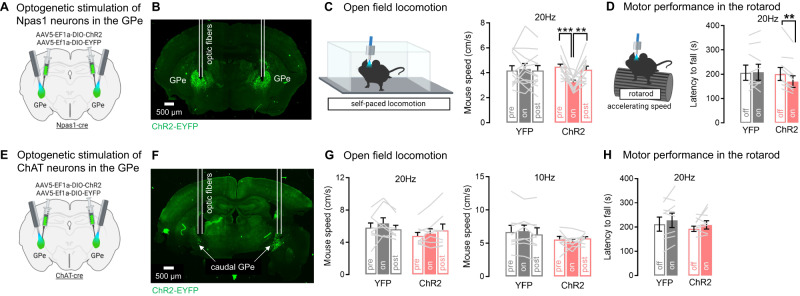
Fig. 9. GPe Npas1 but not ChAT neurons mediate the effects of bridging collaterals on motor function.
A Optogenetic stimulation of globus pallidus externus (GPe) Npas1+ neurons using the optogenetic activator ChR2 B Optic fibers target Npas1 ChR2-YFP+ neurons in the GPe. C Left: 10 trials optogenetic stimulation during open field locomotion. Right: 20 Hz stimulation of Npas1 neurons significantly reduces mouse speed (ANOVA: virus x epoch p < 0.01; Sidak post-hocs ChR2 **p < 0.01, ***<0.001, GFP p > 0.9), N = 12 ChR2, 13 YFP. D Left: Optogenetic stimulation (20 Hz) during rotarod trials at accelerating speed. Right: Stimulation of Npas1 neurons significantly reduces latency to fall (ANOVA: virus x laser p < 0.05; Sidak post-hocs: ChR2 **p < 0.01, GFP p = 0.97), N = 8 ChR2, 9 YFP. E Optogenetic stimulation of GPe choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)+ cholinergic neurons. F Optic fibers target ChAT ChR2-YFP+ neurons in the caudal GPe. G Neither 10 Hz (ANOVA: virus x epoch p = 0.11) or 20 Hz (p = 0.06) ChAT stimulation affects mouse speed, N = 8 ChR2, 8 YFP. H 20 Hz stimulation of ChAT neurons does not affect latency to fall in the rotarod (ANOVA: virus x laser p = 0.63), N = 8 ChR2, 8 YFP. Data are mean ± SEM. Exact p-values are given in Supplementary Dataset S2. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.