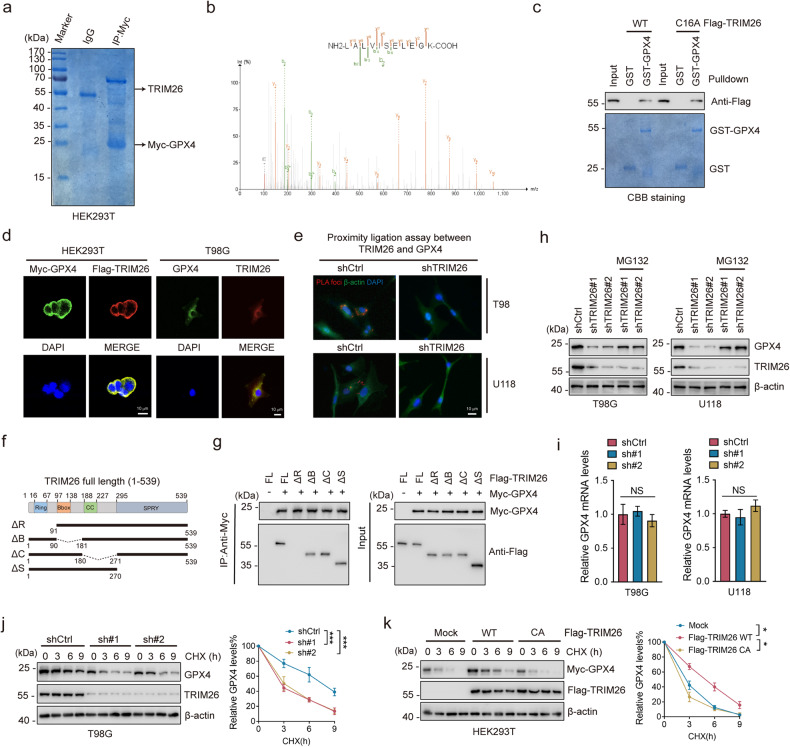
Fig. 1. TRIM26 maintains GPX4 protein stability via direct binding.
a SDS-PAGE and Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) staining of Myc-immunoprecipitated proteins from HEK293T cells stably overexpressing Myc-GPX4. Arrows indicate the proteins of interest. b Peptides of TRIM26 identified by mass spectrometry (MS) analysis. c GST-pulldown assay between TRIM26 and GPX4. Bacterially produced GST control and GST-GPX4 were visualized by CBB staining. Flag-TRIM26 WT or Flag-TRIM26 CA were visualized by gel electrophoresis. d Immunofluorescence (IF) staining of GPX4 (green), TRIM26 (red), and DAPI (blue) in HEK293T and T98G cells. Scale bars, 10 μm. e Images of PLA for endogenous GPX4 and TRIM26 in T98G and U118 cells transfected as indicated. f Sketches of full-length (FL) TRIM26 and four TRIM26 deletion mutants. g Flag-TRIM26 FL or its deletion mutants were co-transfected with the Myc-GPX4 into HEK293T cells. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) using an anti-Myc antibody and then analyzed by immunoblotting (IB). h T98G and U118 cells were transfected with TRIM26 shRNA. After treatment with or without MG132 (20 µM) for 6 h, cell lysates were subjected to IB. i Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) for mRNA levels of GPX4 in T98G and U118 cells transfected with TRIM26 shRNAs or not. j T98G cells transfected with TRIM26 shRNAs were incubated with cycloheximide (CHX) for indicated times, then cell lysates were subjected to IB. Quantification of GPX4 levels relative to β-actin is shown. k Flag-TRIM26 WT or Flag-TRIM26 CA mutant was co-transfected with the Myc-GPX4 into HEK293T cells. After incubation with CHX for indicated times, cells were collected and subjected to IB. Quantification of GPX4 levels relative to β-actin is shown. Data are represented as the mean ± SD (n = 3). One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test (i); student’s t-test (j, k). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, NS: non-significance.