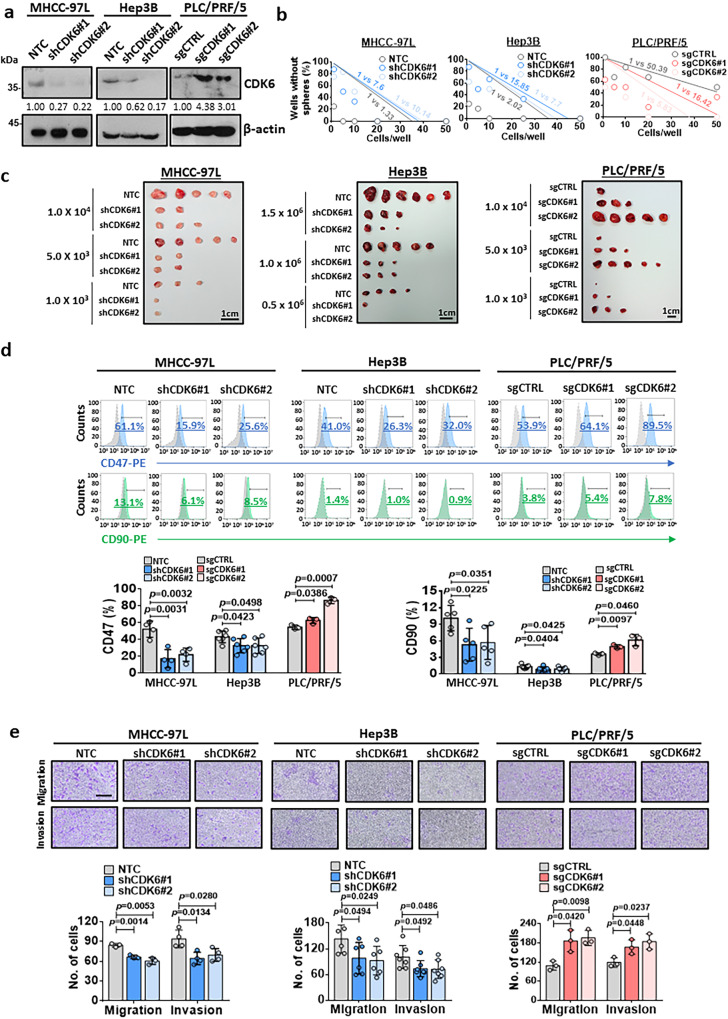
Fig. 2. Critical role of CDK6 in the regulation of liver CSCs.
a The CDK6 protein levels in the non-target control (NTC) and shCDK6 (#1 and #2) MHCC-97L and Hep3B cells as well as in the control (sgCTRL) and sgCDK6 (#1 and #2) subclones derived from PLC/PRF/5 cells were determined by western blot analysis (n = 3 independent experiments). b In vitro limiting dilution sphere analysis showed the role of CDK6 in the regulation of self-renewal ability (n = 2 independent experiments, one-sided extreme limiting dilution analysis). c Left and middle: Knockdown of CDK6 in MHCC-97L and Hep3B cell lines suppressed tumorigenicity compared to NTC cells. Right: Overexpression of CDK6 led to increased tumorigenicity of PLC/PRF/5 cells. Scale bar = 1 cm. d The expression of liver CSC markers, including CD47 (MHCC-97L: n = 4; Hep3B: n = 6 and PLC/PRF/5: n = 3 independent experiments) and CD90 (MHCC-97L: n = 5; Hep3B: n = 7 and PLC/PRF/5: n = 3 independent experiments), was measured by flow cytometry analysis (two-tailed t test). e The migration and invasive abilities of HCC cells were evaluated by uncoated (top; MHCC-97L and PLC/PRF/5: n = 3 and Hep3B: n = 6 independent experiments) and Matrigel-coated transwell (bottom; MHCC-97L: n = 4; Hep3B: n = 7 and PLC/PRF/5: n = 3 independent experiments) assays, respectively. Scale bar = 250 µm. (two-tailed t test). Data was presented as mean ± standard deviation. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.