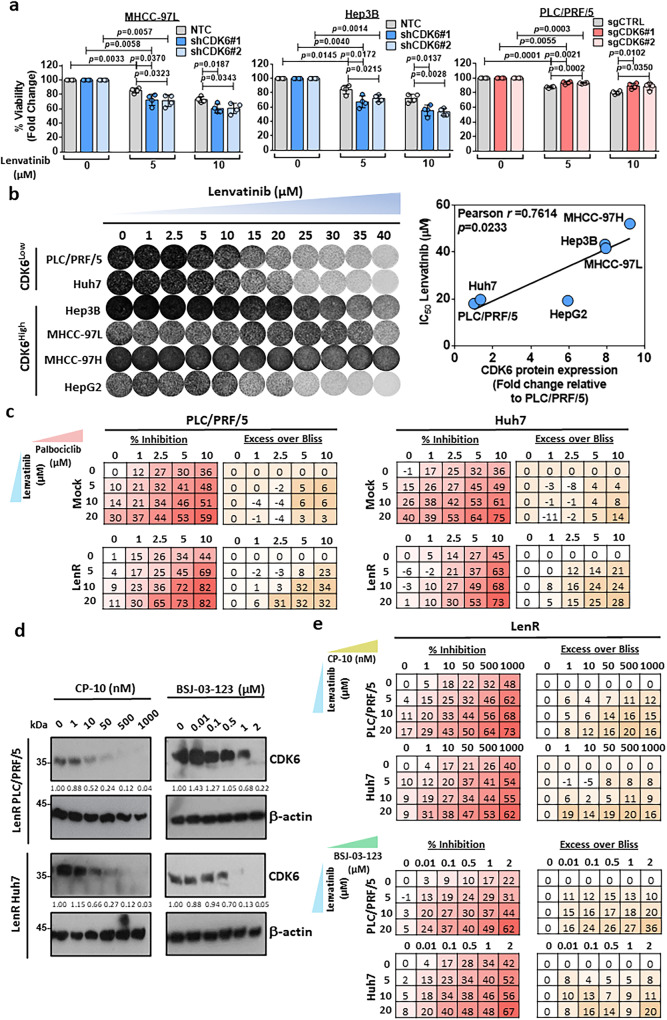
Fig. 4. CDK6 is a critical determinant in lenvatinib resistance.
a The cell viability of shCDK6 (MHCC-97L and Hep3B) and sgCDK6 (PLC/PRF/5) under treatment of lenvatinib (5 µM and 10 µM) for 48 hours was evaluated by MTT assay (n = 4 independent experiments, two-tailed t test). b Long-term colony formation assay of six HCC cell lines. Cells were grown in the absence or presence of lenvatinib at the indicated concentrations for 10–14 days, fixed, and stained. A positive correlation between the IC50 values of lenvatinib and CDK6 protein levels was observed in six HCC cell lines (Pearson r = 0.7614, p = 0.0233). c Combined treatment of lenvatinib and palbociclib synergistically inhibited the growth of mock and lenvatinib-resistant PLC/PRF/5 and Huh7. Cells were treated with the indicated combination at different doses for 48 hours. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay (n = 3 independent experiments). Positive value in excess over Bliss indicated a synergistic effect in the combined treatment. d CP-10 at 50 nM effectively degraded the expression of CDK6 in lenvatinib-resistant PLC/PRF/5 and Huh7 cells, while 2 µM BSJ-03-123 was sufficient to degrade CDK6 in these cells. The protein expression was quantified using ImageJ, normalized to β-actin expression, and expressed as fold-change relative to no treatment control. Representative images of n = 3 independent experiments. e Lenvatinib combined with either CP-10 for 5 days or BSJ-03-123 for 6 days synergistically suppressed the growth of lenvatinib-resistant PLC/PRF/5 and Huh7 cells. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay (n = 3 independent experiments). Positive value in excess over Bliss indicated a synergistic effect in the combined treatment. Data was presented as mean ± standard deviation. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.