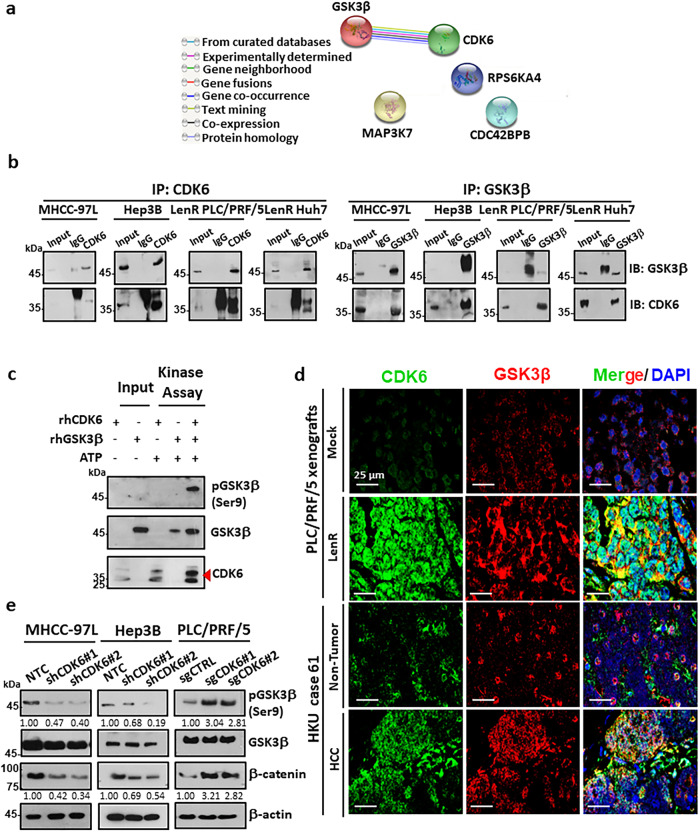
Fig. 6. Physiological significance of the CDK6-GSK3β interaction.
a Protein-protein interactions of enhanced kinases common to lenvatinib-resistant PLC/PRF/5 and Huh7 cells was generated using the STRING database. Lines are colored according to the type of association between the indicated proteins (see legend). b Reciprocal coimmunoprecipitation demonstrated the interaction between endogenous CDK6 and GSK3β in high CDK6-expressing MHCC-97L and Hep3B cells and lenvatinib-resistant cells (n = 2 independent experiments). c Kinase assay using recombinant human CDK6 (rhCDK6) and GSK3β (rhGSK3β) confirmed that GSK3β as a direct substrate of CDK6, as evidenced by the phosphorylation of GSK3β at serine 9 (n = 2 independent experiments). d In a lenvatinib-resistant PLC/PRF/5-derived tumor (n = 1) and HCC clinical tumor specimen (case 61, n = 1), colocalization between CDK6 and GSK3β was observed in HCC cells. CDK6 staining (green), GSK3β staining (red), and DAPI staining (blue). Scale bar = 25 μm. e Western blot analysis of GSK3β, p-GSK3β(Ser9) and β-catenin was performed in CDK6-knockdown and CDK6-overexpressing HCC cells. β-actin was used as a normalization control (n = 3 independent experiments). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.