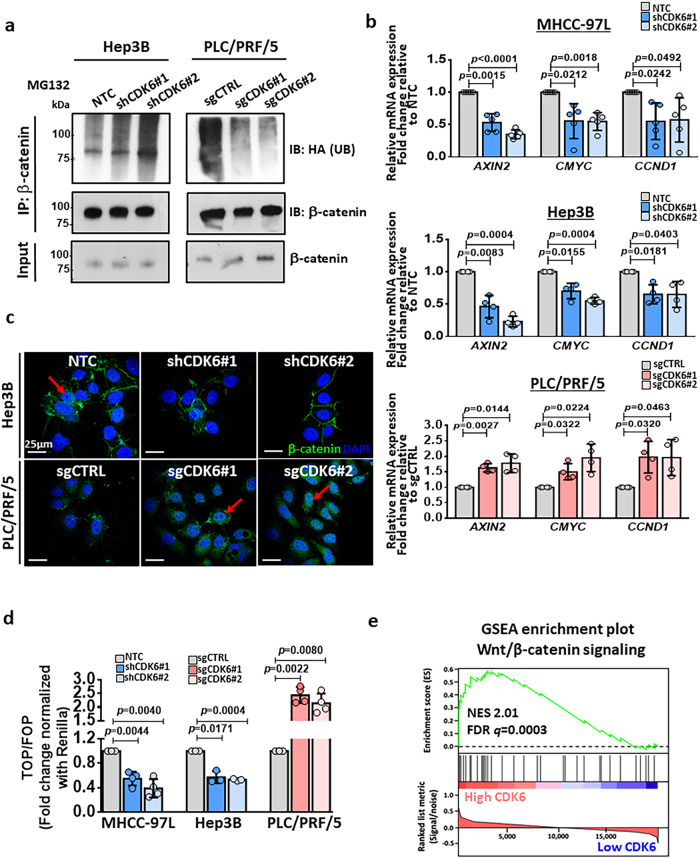
Fig. 7. Functional role of CDK6 in activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling cascade.
a After treatment with 10 μM MG132 for 8 hours, β-catenin was pulled down to investigate the effect of CDK6 on the abundance of ubiquitinated β-catenin. Knockdown of CDK6 promoted the ubiquitination of β-catenin, while overexpression significantly suppressed ubiquitination (IP: β-catenin, IB: HA; n = 3 independent experiments). b The expression of β-catenin downstream genes, including AXIN2, CMYC and CCND2, was examined in CDK6-silencing and overexpressing HCC cells (MHCC-97L: n = 5; Hep3B and PLC/PRF/5: n = 4 independent experiments, two-tailed t test). c The effect of CDK6 alteration on β-catenin accumulation (n = 2 independent experiments). Arrows indicate nuclear expression of β-catenin. β-catenin staining (green) and DAPI staining (blue). Scale bar = 25 μm. d Using the β-catenin TCF binding TOP/FOPFLASH luciferase reporter assay, the transactivating activity of β-catenin was examined in CDK6-knockdown and overexpressing HCC cells (MHCC-97L and PLC/PRF/5: n = 4 and Hep3B: n = 3 independent experiments, two-tailed t test). e By TCGA data analysis, we found that Wnt/β-catenin was enriched in HCC patients with high CDK6 expression with a normalized ES score of 2.011 (FDR q value of 0.0003). Data was presented as mean ± standard deviation. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.