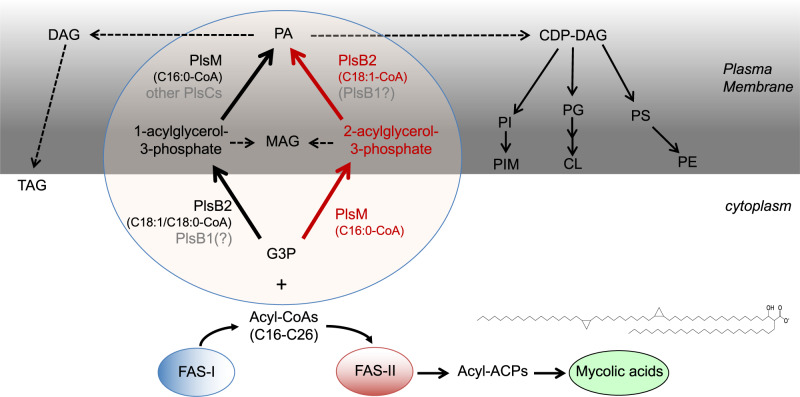
Fig. 8. Proposed pathway for glycerolipid synthesis in mycobacteria.
The proposed steps leading to the biosynthesis of phosphatidic acid (PA) and derived glycerolipids in Mtb based on earlier biochemical studies7 and the present work are shown. The acyl-CoA products of FAS-I serve as the acyl donors in the biosynthesis of PA from glycerol-3-phosphate (G3P). The initial substrates of FAS-II are medium length (C16–C26) keto-acyl-ACP resulting from the condensation of the acyl-CoA products of FAS-I with malonyl-ACP. The processive addition of multiple malonate units to these precursors leads to the elongation of the meromycolate chain (C48–C54) of mycolic acids. The prototypical structure of an Mtb alpha-mycolate is shown. Glycerophospholipids and di- and tri-acylglycerol (DAG and TAG) arise from the central intermediate, PA. The catalytic activity of the enzymes in gray font has not been confirmed. “Other PlsCs” refers, in particular, to Mtb PlsC homologs Rv2483c and Rv3816c which are conserved in other Mycobacterium species, including M. leprae [Table S1]. Other putative PlsC candidates otherwise include Rv3814c, Rv3815c and Rv3026c in Mtb. PS, phosphatidylserine; PI, phosphatidyl-myo-inositol; PIM, phosphatidylinositol mannosides; TAG, triglycerides. Other lipid abbreviations are as in Fig. 6.