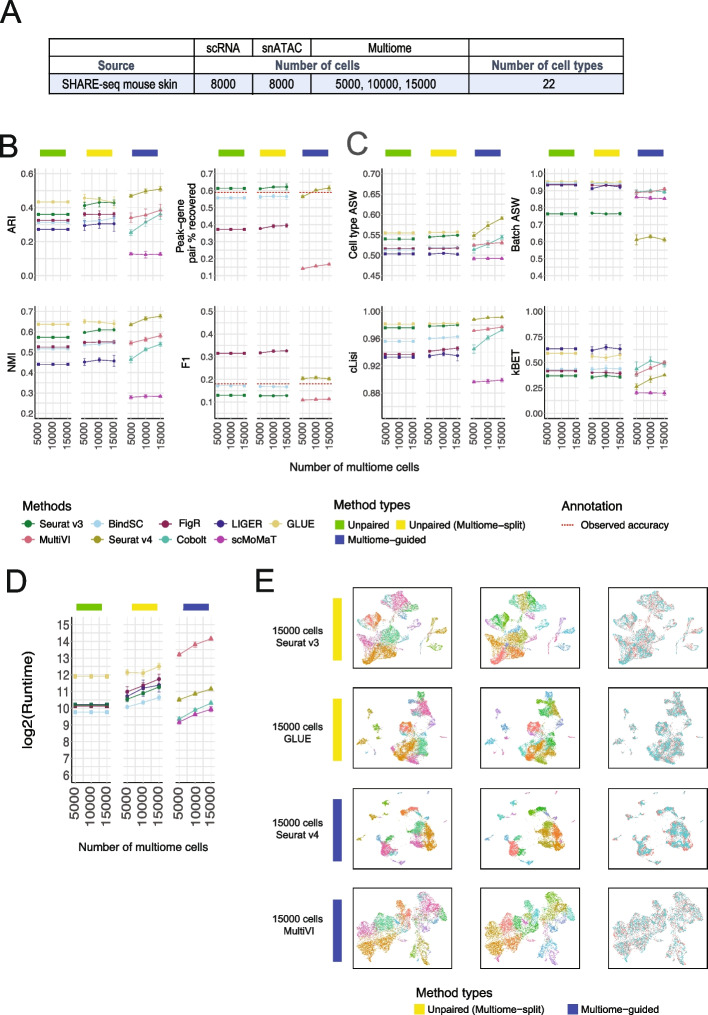
Fig. 3.
Comparison of integration performance without vs. with multiome cells, simulated using the SHARE-seq mouse skin dataset. A The number of cells and cell types for each simulated dataset using the SHARE-seq mouse skin data as the ground truth. B Performance of cell type annotation and peak-gene association recovery. ARI and NMI measure agreement between predicted cell type and ground-truth labels. Peak-gene pair % recovered is the percentage of peak-gene pairs correctly identified compared to the ground-truth list calculated using 32,231 cells from the SHARE-seq dataset. F1 is the prediction accuracy normalized by the number of false positives and false negatives. The dashed line shows the percent recovery and F1 score calculated using 8000 multiome cells. Error bar is mean ± standard deviation. C Performance of cell type separation and batch mixing. Cell type average silhouette width (ASW) and cell type Local Inverse Simpson’s Index (cLISI) measure separation of cell types. Batch ASW and k-nearest neighbor batch effect test (kBET) measure the mixing of scRNA-seq and snATAC-seq cells. Error bar is mean ± standard deviation. D Runtime measured in seconds, for each method, in log2 scale. Error bar is mean ± standard deviation. E UMAP projection using integrated embedding for a select number of methods. UMAP projection for the other methods is shown in Additional file 1: Fig. S6