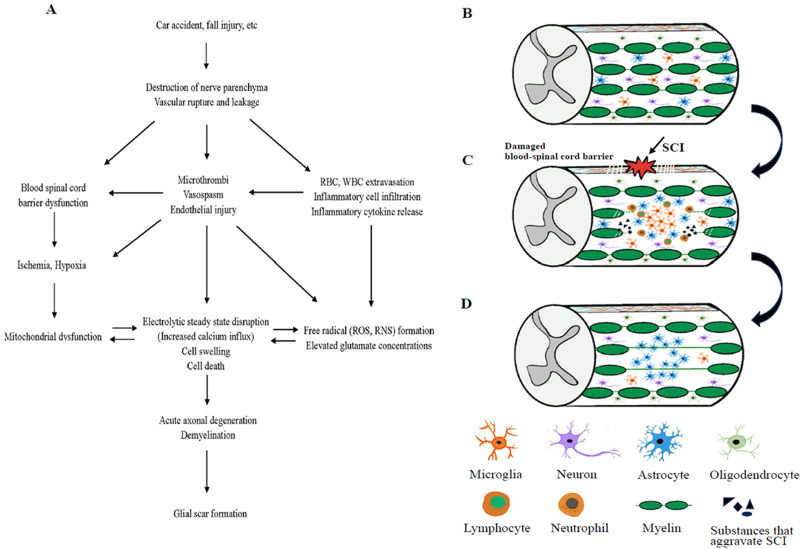
Figure 2.
(A) Pathogenesis of spinal cord injury. (B) Normal spinal cord tissue. (C) When a spinal cord injury occurs, the nerve parenchyma and glial structures are damaged, neutrophils, macrophages/microglia, lymphocytes, etc. infiltrate the injured area, and the concentration of compounds that aggravate spinal cord injury (inflammatory cytokines, reactive oxygen species, tissue-degrading enzymes, etc.) rises. (D) Formation of glial Scar.