Figure 1. Transport of hydrophobic drugs in polymer microchannels.
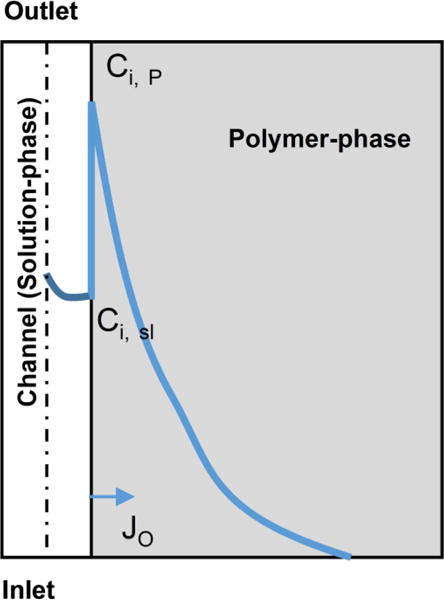
The loss of drug from the solution in the microfluidic channel depends upon all of the following transport processes: 1) convective flux of drug through the microfluidic channel; 2) diffusion of drug in the bulk solution phase, which depends on the diffusion coefficient in solution; 3) the equilibrium concentrations of drug at the interface of polymer-drug solution, which depends on the partition coefficient (K);. 4) Diffusion of drug through the polymer, which depends on the diffusion coefficient in the polymer. Solid blue line represents the concentration profile of a candidate drug from left to right. The loss is proportional to the flux (JO) at the wall indicated by the arrow.
