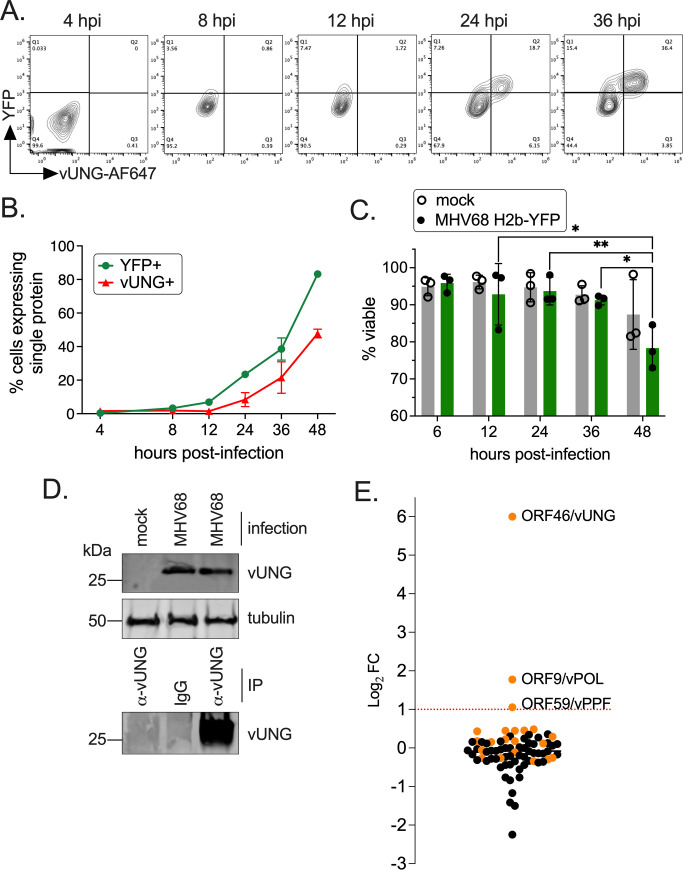
FIG 1.
The MHV68 vUNG interacts with the vPOL and vPPF upon de novo lytic infection. NIH 3T12 cells were infected with MHV68 H2b-YFP at an MOI of 3.0. (A) Cells were fixed and stained for flow cytometry at the indicated hpi. Plots indicate the gating strategy used to identify YFP+ infected cells on the y-axis and cells expressing vUNG detected by the vUNG-C1 mAb conjugated to AF647+ on the x-axis. (B) Line graph of percentage of cells with YFP or vUNG from flow data collected in (A). (C) Cell viability of mock and infected cells was measured by exclusion of propidium iodide by flow cytometry. Symbols represent three biological replicates ±SEM. Statistical significance was evaluated by a two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (D) Immunoprecipitation of the vUNG using the vUNG-C1 mAb from infected NIH 3T12 cells at 36 hpi. (E) Enriched peptides identified by mass spectrometry with a Log2 fold change following IP of vUNG compared to control IgG. The orange spheres denote MHV68-specific peptides detected, while the black spheres denote host/murine peptides.