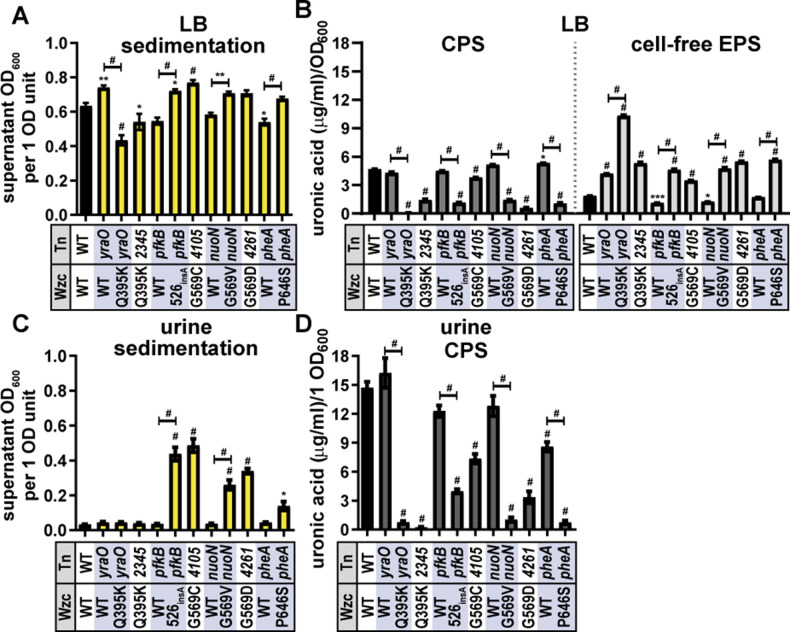
Fig 4.
Tn:mucoid+ strains impact sedimentation resistance and EPS production. K. pneumoniae strain KPPR1 Tn:mucoid+ or Tn:mucoidWT strains were cultured in (A and B) LB medium or (C and D) sterile-filtered human urine. The transposon (Tn) insertion site is listed on the X-axis along with the Wzc variant listed below (WT = wild type). (A and C) Mucoidy was determined by quantifying the supernatant OD600 after sedimenting 1 OD600 unit of culture at 1,000 × g for 5 min. (B) The uronic acid content of the total culture or supernatant (light gray, right) was quantified and normalized to the OD600 of the overnight culture. The cell-associated CPS (dark gray, left) was deduced by subtracting the cell-free uronic acid content (EPS) from the total culture uronic acid content. (D) Urine contains high levels of uronic acid-conjugated molecules. To eliminate this background signal, 1 OD600 unit of bacteria was washed in sterile PBS, and then the cell-associated uronic acid content was quantified. Data presented are the mean, and error bars represent the standard error of the mean. Statistical significance was determined using two-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni post-test to compare specific groups. *P < 0.0332; **P < 0.0021; ***P < 0.0002; # P < 0.0001. Experiments were performed ≥3 independent times, in triplicate.