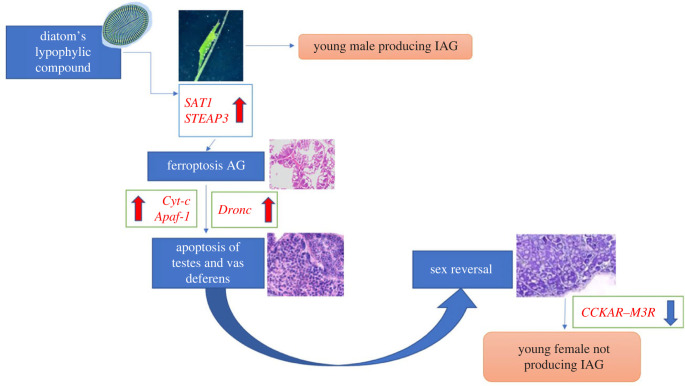
Figure 6.
Representation of the main processes derived from the analysis of the transcriptome of H. inermis upon the ingestion of Cocconeis spp. The lipophilic compound present in the diatoms (as modelled by DGLA) activates SAT1 (Spermidine/Spermine N1-Acetyltransferase 1) and STEAP3 (Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate 3 metalloreductase) genes, inducing a process of ferroptosis specifically in the tissues of the rudimentary androgenic gland of 5-day-old post-larvae. Following the destruction of the androgenic gland, male primary and secondary sex characters, including the testes and vasa deferentia, undergo a process of apoptosis, starting with the upregulation of the electron carriers Cyt-c and Apaf-1, which in turn triggers the activation of the Dronc initiator, leading to a complete sex shift. The production of the IAG hormone is stopped through the downregulation of CCKAR and M3R. According to this scheme, following the apoptosis of the male reproductive system (primed by ferroptosis specifically destroying the AG tissues), the sex reversal occurs, and the female reproductive system develops.