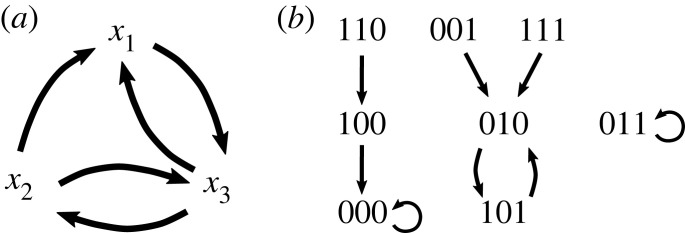
Figure 1.
Wiring diagram and state space of the Boolean network . (a) The wiring diagram encodes the dependency between variables. Subnetworks are defined on the basis of the wiring diagram. For example, the subnetwork is the restriction of F to {x2, x3} and contains external parameter x1. (b) The state space is a directed graph with edges between all states and their images. This graph, therefore, encodes all possible trajectories and attractors. Here, F has two steady states, 000 and 011, and one limit cycle, (010, 101), so .